pt-BR
nomes no trilho de navegação

Els gammaproteobacteris (Gammaproteobacteria) és una classe de diversos grups de bacteris importants per la ciència i la medicina com són els Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae i Pseudomonadaceae. Molts patògens pertanyen a aquesta classe, per exemple Salmonella (enteritis i febre tifoidea), Yersinia (plaga), Vibrio (còlera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infeccions hospitalàries o fibrosi quística). Com tots els proteobacteria, els gammaproteobacteria són gram-negatius.
Els gammaproteobacteris (Gammaproteobacteria) és una classe de diversos grups de bacteris importants per la ciència i la medicina com són els Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae i Pseudomonadaceae. Molts patògens pertanyen a aquesta classe, per exemple Salmonella (enteritis i febre tifoidea), Yersinia (plaga), Vibrio (còlera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infeccions hospitalàries o fibrosi quística). Com tots els proteobacteria, els gammaproteobacteria són gram-negatius.
Gammaproteobacteria (auch γ-Proteobacteria) bezeichnet eine Klasse im phylogenetischen System der Bakterien, das auf der Grundlage der Basensequenz der ribosomalen 16S-Ribonukleinsäure (16S-rRNA) und anderer phylogenetischer Methoden aufgestellt wurde. Das Phylum (der Stamm) Proteobacteria wird in die fünf Klassen Alphaproteobacteria bis Epsilonproteobacteria eingeteilt (Stand 2005). In den letzten Jahren sind noch drei weitere Klassen beschrieben worden (Stand 2019), die „Zetaproteobacteria“, Acidithiobacillia und Oligoflexia. Alle Vertreter dieses Stammes sind gramnegativ.
Zu den Gammaproteobacteria gehören die folgenden Ordnungen (Stand 2019)[1]
Der Artikel Systematik der Bakterien gilt in der Wikipedia als Referenz und enthält eine größere Auswahl an Taxa in der Klasse Gammaproteobacteria.
Die Ordnung Xanthomonadales wurde aufgelöst, die verschiedenen Gattungen wurden zu anderen Ordnungen (unter anderem die Ordnung Lysobacterales) gestellt oder werden zurzeit noch keiner genaueren Ordnung zugestellt. Die Ordnung Acidithiobacillales wurde 2013 in die neu geschaffene Klasse Acidithiobacillia übertragen.[2] 2016 wurde die Ordnung Enterobacterales (Enterobakterien) etabliert, vorher wurde für diese Bakteriengruppe der Name „Enterobacteriales“ verwendet, der jedoch nach den Regeln des Bakteriologischen Codes (ICBN) nicht gültig war. Weiterhin gab es nur eine Familie – die Enterobacteriaceae – innerhalb der Ordnung. Mit der Etablierung der Ordnung Enterobacterales verbunden ist eine Aufteilung der bisher bekannten Taxa auf mehrere neue Familien.[3]
Die Gammaproteobacteria bilden derzeit die artenreichste Klasse der Proteobacteria. Sie sind physiologisch außerordentlich divers und vereinen eine Vielzahl sehr unterschiedlicher Stoffwechseltypen. Gleichzeitig sind viele Gattungen physiologisch flexibel und anpassungsfähig. In den Gattungen Legionella, Pseudomonas, Vibrio, Salmonella und Shigella findet man wichtige Krankheitserreger von Mensch, Tier und Pflanze.
Wichtige Vertreter sind unter anderem in den Gattungen Chromatium, Xanthomonas, Beggiatoa, Legionella, Pseudomonas, Azotobacter und Vibrio sowie in der Ordnung Enterobacterales mit den Gattungen Enterobacter, Escherichia, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia, Shigella, Yersinia (und anderen) zu finden.
Für die 2019 zunächst im meromiktischen Zugersee, dann auch in Frankreich, Taiwan und Ostafrika gefundene Gruppe um den Endosymbionten Candidatus Azoamicus ciliaticola wurde 2021 eine neue Ordnung innerhalb der Gammaproteobacteria mit der provisorischen Bezeichnung eub62A3 group (alias Candidatus Azoamicus group) vorgeschlagen, zusammen mit zwei Untergruppen A (nächst Ca. A. ciliaticola) und B.
Ca. A. ciliaticola lebt endosymbiotisch in Wimpertierchen (Ciliophora) der Klasse Plagiopylea. Er kann Denitrifikation zur Gewinnung von Energie verwenden, die er seinem Wirt zur Verfügung stellt.[4]
Gammaproteobacteria (auch γ-Proteobacteria) bezeichnet eine Klasse im phylogenetischen System der Bakterien, das auf der Grundlage der Basensequenz der ribosomalen 16S-Ribonukleinsäure (16S-rRNA) und anderer phylogenetischer Methoden aufgestellt wurde. Das Phylum (der Stamm) Proteobacteria wird in die fünf Klassen Alphaproteobacteria bis Epsilonproteobacteria eingeteilt (Stand 2005). In den letzten Jahren sind noch drei weitere Klassen beschrieben worden (Stand 2019), die „Zetaproteobacteria“, Acidithiobacillia und Oligoflexia. Alle Vertreter dieses Stammes sind gramnegativ.
Gammaproteobacteria es un classe de Proteobacteria.
Ang Gammaproteobacteria ay isang klase sa Proteobacteria na kung saan kinabibilangan ng Enterobacteria.
![]() Ang lathalaing ito na tungkol sa Agham ay isang usbong. Makatutulong ka sa Wikipedia sa nito.
Ang lathalaing ito na tungkol sa Agham ay isang usbong. Makatutulong ka sa Wikipedia sa nito.
Гама протеобактерии (Gammaproteobacteria) — класа на неколку медицински и научно значајни групи на бактерии, како што е групата Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae и Pseudomonadaceae. Голем број на значајни патогени исто така припаѓаат на оваа група, како на пример, Salmonella (ентеритис и тифусна треска), Yersinia (чума), Vibrio (колера), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (белодробни инфекции кај хоспитализирани пациенти или пациенти со цистична фиброза), додека еден сој на E. coli предизвикува труење со храна. Членовите на родот Chromatium се фотосинтетски и го оксидираат водород сулфидот (наместо водата) и даваат сулфур како екскрет. Некои гама протеобактерии го оксидираат метанот и многу од нив живеат во симбиоза со животните од геотермалните океански топли извори.[1]
Некои поважни фамилии од оваа група се:
Гама протеобактерии (Gammaproteobacteria) — класа на неколку медицински и научно значајни групи на бактерии, како што е групата Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae и Pseudomonadaceae. Голем број на значајни патогени исто така припаѓаат на оваа група, како на пример, Salmonella (ентеритис и тифусна треска), Yersinia (чума), Vibrio (колера), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (белодробни инфекции кај хоспитализирани пациенти или пациенти со цистична фиброза), додека еден сој на E. coli предизвикува труење со храна. Членовите на родот Chromatium се фотосинтетски и го оксидираат водород сулфидот (наместо водата) и даваат сулфур како екскрет. Некои гама протеобактерии го оксидираат метанот и многу од нив живеат во симбиоза со животните од геотермалните океански топли извори.
गामाप्रोटियोबैक्टीरिया (Gammaproteobacteria) बैक्टीरिया का एक जीववैज्ञानिक वर्ग है, जिसमें कई चिकित्सा, पारिस्थितिकी और अन्य वैज्ञानिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण जातियाँ और हैजा फैलाने वाले वाइब्रियो कोलेराए (Vibrio cholerae) जैसी कुछ रोगजनक जातियाँ भी सम्मिलित हैं। अन्य प्रोटियोबैक्टीरिया वर्गों की तरह गामाप्रोटियोबैक्टीरिया भी ग्राम-ऋणात्मक होते हैं।[1][2]
गामाप्रोटियोबैक्टीरिया (Gammaproteobacteria) बैक्टीरिया का एक जीववैज्ञानिक वर्ग है, जिसमें कई चिकित्सा, पारिस्थितिकी और अन्य वैज्ञानिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण जातियाँ और हैजा फैलाने वाले वाइब्रियो कोलेराए (Vibrio cholerae) जैसी कुछ रोगजनक जातियाँ भी सम्मिलित हैं। अन्य प्रोटियोबैक्टीरिया वर्गों की तरह गामाप्रोटियोबैक्टीरिया भी ग्राम-ऋणात्मक होते हैं।
Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria). It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genus-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes.[1] Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. It is composed by all Gram-negative microbes and is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of Proteobacteria.[2]
These microorganisms can live in several terrestrial and marine environments, in which they play various important roles, including extreme environments such as hydrothermal vents. They generally have different shapes - rods, curved rods, cocci, spirilla, and filaments[3] and include free living bacteria, biofilm formers, commensals and symbionts,[4] some also have the distinctive trait of being bioluminescent.[5] Metabolisms found in the different genera are very different; there are both aerobic and anaerobic (obligate or facultative) species, chemolithoautotrophics, chemoorganotrophics, photoautotrophs and heterotrophs.[6]
The element "gamma" (third letter of the Greek alphabet) indicates that this is Class III in Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology (Vol. II, page 1). Proteus refers to the Greek sea god who could change his shape. Bacteria (Greek βακτήριον; "rod" "little stick"), in terms of etymological history, refers to Bacillus (rod-shaped bacteria), but in this case is "useful in the interim while the phylogenetic data are being integrated into formal bacterial taxonomy."[7]
Currently, many different classifications are based on different approaches, such as the National Center for Biotechnology Information, based on genomic, List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature , ARB-Silva Database[8] based on ribosomal RNA, or a multiprotein approach. It is still very difficult to resolve the phylogeny of this bacterial class.[9]
Here, it is reported a clade based on a set of 356 protein families for the class of Gammaproteobacteria.
Phylogeny of Gammaproteobacteria GammaproteobacteriaRuthia, Vesicomyosocius, Thiomicrospira, Dichelobacter, Francisella
Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Alteromonas, Idiomarinaceae
Phylogeny of Gammaproteobacteria after[10] Not all orders are monophyletic, consequently families or genera are shown for the Pseudomonadales, Oceanospirillales, and Alteromonadales. In the case of singleton orders, the genus is shown. (In bacterial taxonomy, orders have the suffix -ales, while families have -aceae.)A number of bacteria have been described as members of the Gammaproteobacteria, but have not yet been assigned an order or family. These include bacteria of the genera Alkalimonas, Gallaecimonas, Ignatzschineria, Litorivivens, Marinicella, Plasticicumulans, Pseudohongiella, Sedimenticola, Thiohalobacter, Thiohalorhabdus, Thiolapillus, and Wohlfahrtiimonas.[11]
Gammaproteobacteria, especially the orders Alteromonadales and Vibrionales, are fundamental in marine and coastal ecosystems because they are the major groups involved in the nutrients cycling[12] and despite their fame as pathogens, they find application in a huge number of fields, such as bioremediation and biosynthesis.
Gammaproteobacteria can be used as a microbial fuel cell (MFC)[13] element that applies their ability to dissimilate various metals.[14] The produced energy could be collected as one of the most environmentally friendly and sustainable energy production systems.[15] They are also used as biological methane filters.[16]
Phototrophic purple sulfur bacteria are used in wastewater treatment processes[17] and the ability of some Gammaproteobacteria (e.g. the genus Alcanivorax[18]) to bioremediate oil is becoming increasingly important to degrade crude oil after oil spills.[19] Some species from the family Chromatiaceae are notable because might be involved in the production of vitamin B12.[20] Another application of some Gammaproteobacteria is their ability to synthesize Poly-b-hydroxyalkanoate (PHA)[21] which is a polymer that is used in the production of biodegradable plastics. Also lots of Gammaproteobacteria species are able to generate secondary metabolites with antibacterial properties.[22]
Gammaproteobacteria are widely distributed and abundant in various ecosystems such as soil, freshwater lakes and rivers, oceans and salt lakes. For example, Gammaproteobacteria constitute about 6–20% (average of 14%) of bacterioplankton in different oceans;[23] plus, current researches have revealed their worldwide propagation in deep-sea and coastal sediments.[24] In seawater, Bacterial community composition could be shaped by miscellaneous environmental parameters, such as phosphorus, total organic carbon contents, salinity, and pH,[25] and the higher is the soil pH, the higher is the relative abundance of Alphaproteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria.[26] The relative abundance of Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria is also positively correlated to the dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration, which is a key environmental parameter shaping bacterial community composition.[27] Gammaproteobacteria are also key players in the dark carbon fixation in coastal sediments, which are the largest carbon sink on Earth and the majority of these bacteria have not been cultured yet.[28] The deep-sea hydrothermal system is one of the most extreme environments on Earth. Almost all vent-endemic animals are strongly associated with the primary production of the endo- and/or episymbiotic chemoautotrophic microorganisms.[29] Analyses of both the symbiotic and free-living microbial communities in the various deep-sea hydrothermal environments have revealed a predominance in biomass of members of the Gammaproteobacteria.[30]
Gammaproteobacteria have a wide diversity, metabolic versatility, and functional redundancy in the hydrothermal sediments, and they are responsible for the important organic carbon turnover and nitrogen and sulfur cycling processes.[31] Anoxic hydrothermal fluids contain several reduced compounds such as H2, CH4, and reduced metal ions in addition to H2S. It has been proposed that hydrogen sulfide-oxidizing and oxygen- reducing chemoautotrophs potentially sustain the primary production in these unique ecosystems.[32] In the last decades, it has been found that orders belonging to Gammaproteobacteria, like Pseudomonas, Moraxella, are able to degrade different types of plastics and these microbes might have a key role in plastic biodegradation.[33]
In the class of Gammaproteobacteria there is a wide diversity of metabolisms.
Some groups are nitrite-oxidizers[34] and ammonia oxidizers like the members of Nitrosococcus - with the exception of Nitrosococcus mobilis - and they are also obligate halophilic bacteria. [35]
Among Gammaproteobacteria there are chemoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing groups, like Thiotrichales, which are found as microbial biofilm filamentous communities in the Tor Caldara shallow-water gas vent in the Tyrrhenian sea .[36] Moreover, thanks to 16S rRNA gene analysis, different sulfide oxidizers in the Gammaporteobacteria class have been detected, and the most important among them are Beggiatoa, Thioploca and Thiomargarita; besides, large amounts of hydrogen sulfide are produced by sulfate-reducing bacteria in organic-rich coastal sediments.[37]
Marine Gammaproteobacteria also include aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria (AAP) that use bacteriochlorophyll to support the electron transport chain. They are believed to be an essential community in the oceans and are also well spread all around. [38]
Another type of metabolism carried out by Gammaproteobacteria is the oxidation of Methane, carried out by the order Methylococcales. They metabolize methane as sole energy source and are very important in the global carbon cycle. They are found in any site where methane sources are, like gas reserves, soils, wastewaters. [39]
Purple sulfur bacteria are anoxygenic phototrophic iron‐oxidizers and they are part of the genus[40] Acidithiobacillus but, there are also two strains of Thiodictyon (Chromatiales order) -strain L7 and strain F4- and few species within the genus Thermomonas (order Lysobacter) that carry out the same metabolism.[41]
In this class, there are numerous genera of obligate and generalist hydrocarbonclastic bacteria. The obligate hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria (OHCB) share the ability to utilize hydrocarbons almost exclusively as a carbon source and until now they have been found only in the marine environment. The genera carrying out this metabolism are Alcanivorax, Oleiphilus, Oleispira, Thalassolitus, Cycloclasticus and Neptunomonas. Subsequently, additional species such as Polycyclovorans, Algiphilus of the order Xanthomonadales and Porticoccus hydrocarbonoclasticus of the order Cellvibrionales that were isolated from phytoplankton. Groups of aerobic “generalist” hydrocarbon degraders can utilize hydrocarbons and nonhydrocarbon substrates as source of carbon and energy and are members within the genera Acinetobacter, Colwellia, Glaciecola, Halomonas, Marinobacter, Marinomonas, Methylomonas, Pseudoalteromonas, Pseudomonas, Rhodanobacter, Shewanella, Stenotrophomonas, and Vibrio.[42]
The most frequent pathway to synthesize glucose among Gammaporteobacteria members is Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle but, a minority of species of this class may use the rTCA cycle.[43] Thioflavicoccus mobilis (free living gammaproteobacteria) and "Candidatus Endoriftia persephone" (symbiont of the giant tubeworm Riftia pachyptila), present the possibility of using the rTCA cycle in addition to the CBB cycle. It has been showed that some species of Gammaproteobacteria may express two different carbon fixation pathways simultaneously.[44]
Symbiosis is a close and a long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms. A large number of Gammaproteobacteria are able to join in a close endosymbiosis with various species. Evidence for this can be found in a wide variety of ecological niches: on the ground,[45][46] within plants,[47] or deep on the ocean floor.[48] On the land, it has been reported that Gammaproteobacteria species have been isolated from Robinia pseudoacacia[49] and other plants,[50][51] while in the deep sea a sulfur-oxidizing gammaproteobacteria was found in a hydrothermal vent chimney;[52] by entering into symbiotic relationships in deep sea areas, sulfur-oxidizing chemolithotrophic microbes receive additional organic hydrocarbons in hydrothermal ecosystems. Some Gammaproteobacteria are symbiotic with geothermic ocean vent-downwelling animals[53], and in addition, Gammaproteobacteria can have complex relationships with other species that live around thermal springs,[54] for example, with the shrimp Rimicaris exoculata living from hydrothermal vents on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Regarding the endosymbionts, most of them lack many of their family characteristics due to significant genome reduction.[55][56]
Gammaproteobacteria comprise several medically and scientifically important groups of bacteria, such as the families Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae, and Pseudomonadaceae. A number of human pathogens belong to this class, including Yersinia pestis, Vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and some species of Salmonella. The class also contains plant pathogens such as Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (citrus canker), Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae (kiwifruit Psa outbreak), and Xylella fastidiosa. In the marine environment, several species from this class can infect different marine organisms, such as species in the genus Vibrio which affect fish, shrimp, corals or oysters,[57] and species of Salmonella which affect grey seals (Halichoerus grypus).[58][59]
Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria). It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genus-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. It is composed by all Gram-negative microbes and is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of Proteobacteria.
These microorganisms can live in several terrestrial and marine environments, in which they play various important roles, including extreme environments such as hydrothermal vents. They generally have different shapes - rods, curved rods, cocci, spirilla, and filaments and include free living bacteria, biofilm formers, commensals and symbionts, some also have the distinctive trait of being bioluminescent. Metabolisms found in the different genera are very different; there are both aerobic and anaerobic (obligate or facultative) species, chemolithoautotrophics, chemoorganotrophics, photoautotrophs and heterotrophs.
Gammaproteobacteria (también Gamma Proteobacteria o γ-bacteria) son una clase de bacterias que incluye diversas especies de importancia médica, ecológica y científica, como las enterobacterias (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae, Pseudomonadaceae y Klebsiella pneumoniae (neumonía).
Igual que todas las proteobacterias, las Gammaproteobacteria son Gram negativas.
A esta clase pertenece gran cantidad de patógenos importantes, tales como Salmonella (enteritis y fiebre tifoidea), Yersinia (peste), Vibrio (cólera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infecciones intrahospitalarias o en pacientes con fibrosis quística).
Como ya se mencionó, Gammaproteobacteria comprende bacterias de importancia médica y científica como Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae y Pseudomonadaceae.
Un número importante de patógenos comunes pertenecen a esta clase; v. gr.: Salmonella spp. (enteritis y fiebre tifoidea), Yersinia pestis (peste), Vibrio cholerae (cólera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infección nosocomial o en pacientes con fibrosis quística) y Escherichia coli (intoxicación alimentaria).
Miembros del género Chromatium realizan fotosíntesis, oxidan ácido sulfhídrico («sulfuro de hidrógeno») y, en lugar de agua, generan azufre como excremento. Algunas gammaproteobacterias oxidan metano. Muchas existen en simbiosis con animales moradores en fuentes hidrotermales de ventilas oceánicas.[1]
La filogenia de Gammaproteobacteria es difícil de resolver. El análisis multiproteínico ha dado el siguiente resultado:[2]
GammaproteobacteriaRuthia, Vesicomyosocius, Thiomicrospira, Dichelobacter, Francisella
Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Alteromonas, Idiomarinaceae
Gammaproteobacteria (también Gamma Proteobacteria o γ-bacteria) son una clase de bacterias que incluye diversas especies de importancia médica, ecológica y científica, como las enterobacterias (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae, Pseudomonadaceae y Klebsiella pneumoniae (neumonía).
Igual que todas las proteobacterias, las Gammaproteobacteria son Gram negativas.
A esta clase pertenece gran cantidad de patógenos importantes, tales como Salmonella (enteritis y fiebre tifoidea), Yersinia (peste), Vibrio (cólera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infecciones intrahospitalarias o en pacientes con fibrosis quística).
Gammaproteobakterioak, Gamma proteobakterio eta γ proteobakterio ere deituak, garrantzi mediko, ekologiko eta zientifikoa duten zenbait espezie hartzen dituen bakterio klase bat dira. Klase honetakoak dira, esate baterako, Escherichia coli bezalako enterobakterioak, Vibrionaceae eta Pseudomonaceae generoetako bakterioak eta pneumonia eragiten duen Klebsiella pneumoniae bakterioa.
Proteobakterio guztiak bezala, gammaproteobakterioak Gramnegatiboak dira.
Klase honetakoak dira gaixotasunak eragiten dituzten bakterio asko. Horien artean Salmonella (enteritisa eta sukar tifoidea, Yersinia (izurria), Vibrio (kolera eta Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ospitaletan gertatzen diren infekzioen edo fibrosi kistikoa duten gaixoek jasaten dituzten infekzioen sortzailea).
Aipatu bezala, Gammaproteobakterioen klaseak garrantzi medio eta zientifikoko bakterioak hartzen ditu bere barne, Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae eta Pseudomonaceae generoetakoak kasu.
Ruthia, Vesicomyosocius, Thiomicrospira, Dichelobacter, Francisella
Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Alteromonas, Idiomarinaceae
Gammaproteobakterioak, Gamma proteobakterio eta γ proteobakterio ere deituak, garrantzi mediko, ekologiko eta zientifikoa duten zenbait espezie hartzen dituen bakterio klase bat dira. Klase honetakoak dira, esate baterako, Escherichia coli bezalako enterobakterioak, Vibrionaceae eta Pseudomonaceae generoetako bakterioak eta pneumonia eragiten duen Klebsiella pneumoniae bakterioa.
Proteobakterio guztiak bezala, gammaproteobakterioak Gramnegatiboak dira.
Klase honetakoak dira gaixotasunak eragiten dituzten bakterio asko. Horien artean Salmonella (enteritisa eta sukar tifoidea, Yersinia (izurria), Vibrio (kolera eta Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ospitaletan gertatzen diren infekzioen edo fibrosi kistikoa duten gaixoek jasaten dituzten infekzioen sortzailea).
Gammaproteobacteria eli gammaproteobakteerit on bakteerien tieteellisen luokittelun luokka. Luokkaan kuuluu joitakin lääketieteellisesti, ekologisesti ja tieteellisesti tärkeitä bakteeriryhmiä, kuten enterobakteeirt (Enterobacteriales), joista tunnetuin lienee kolibakteeri. Myös salmonellat kuuluvat tähän bakteeriluokkaan. Kuten kaikki proteobakteerit, myös gammaproteobakteerit ovat gramnegatiivisia. Luokkaan kuuluu myös monia merkittäviä keuhkokuumetta aiheuttavia bakteereja.
Gammaproteobacteria eli gammaproteobakteerit on bakteerien tieteellisen luokittelun luokka. Luokkaan kuuluu joitakin lääketieteellisesti, ekologisesti ja tieteellisesti tärkeitä bakteeriryhmiä, kuten enterobakteeirt (Enterobacteriales), joista tunnetuin lienee kolibakteeri. Myös salmonellat kuuluvat tähän bakteeriluokkaan. Kuten kaikki proteobakteerit, myös gammaproteobakteerit ovat gramnegatiivisia. Luokkaan kuuluu myös monia merkittäviä keuhkokuumetta aiheuttavia bakteereja.
Les Gammaproteobacteria sont l'un des cinq groupes de Proteobacteria, relativement ubiquiste, retrouvés jusque dans les nuages, pluies et brouillards[2],[3].
Il comprend :
Les Gammaproteobacteria sont l'un des cinq groupes de Proteobacteria, relativement ubiquiste, retrouvés jusque dans les nuages, pluies et brouillards,.
As gammaproteobacterias ou Gammaproteobacteria (ás veces escrito gamma-proteobacterias ou proteobacterias gamma) son un grupo de bacterias gramnegativas considerado unha clase dentro do filo Proteobacteria. Comprende bacterias importantes desde o punto de vista médico, ecolóxico e científico, como as Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae e Pseudomonadaceae. Un gran número de patóxenos importantes pertencen a esta clase, como por exemplo, Salmonella (enterites e febres tifoides), Yersinia (peste bubónica), Vibrio (cólera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infeccións pulmonares hospitalarias ou que afectan a pacientes de fibrose quística), e Klebsiella pneumoniae responsable de causar pneumonías. Tamén comprende un xénero que leva o nome de Galicia, Gallaecimonas.
Membros do xénero Chromatium son fotosintéticos e utilizan o sulfuro de hidróxeno en troques da auga na súa fotosíntese, expulsando xofre. Algunhas Gammaproteobacteria oxidan metano, e moitas delas viven en simbiose con animais que habitan chemineas oceánicas xeotérmicas.[1]
As gammaproteobacterias son parafiléticas das betaproteobacterias por culpa de que inclúen o xénero Acidithiobacillus (ver Proteobacteria).
Móstrase a filoxenia das Gammaproteobacteria segundo a Filoxenia de gammaproteobacterias de K.P. Williams et al.[2] Non todas as ordes son monofiléticas (as ordes terminan en -ales). Para as Pseudomonadales, Oceanospirillales e Alteromonadales móstranse as familias (terminación -aceae) e xéneros. Noutras ordes só se indica un xénero.
Ruthia, Vesicomyosocius, Thiomicrospira, Dichelobacter, Francisella
Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Alteromonas, Idiomarinaceae
As gammaproteobacterias ou Gammaproteobacteria (ás veces escrito gamma-proteobacterias ou proteobacterias gamma) son un grupo de bacterias gramnegativas considerado unha clase dentro do filo Proteobacteria. Comprende bacterias importantes desde o punto de vista médico, ecolóxico e científico, como as Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae e Pseudomonadaceae. Un gran número de patóxenos importantes pertencen a esta clase, como por exemplo, Salmonella (enterites e febres tifoides), Yersinia (peste bubónica), Vibrio (cólera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infeccións pulmonares hospitalarias ou que afectan a pacientes de fibrose quística), e Klebsiella pneumoniae responsable de causar pneumonías. Tamén comprende un xénero que leva o nome de Galicia, Gallaecimonas.
Membros do xénero Chromatium son fotosintéticos e utilizan o sulfuro de hidróxeno en troques da auga na súa fotosíntese, expulsando xofre. Algunhas Gammaproteobacteria oxidan metano, e moitas delas viven en simbiose con animais que habitan chemineas oceánicas xeotérmicas.
I Gammaproteobacteria sono una classe di batteri, rilevante sia sotto il punto di vista medico che scientifico. Un certo numero di importanti batteri patogeni appartiene a questa classe, ad esempio la salmonella (responsabile di enteriti e febbri tifoidi), Yersinia pestis (agente patogeno della peste), Vibrio cholerae (vibrione che provoca il colera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infezioni polmonari e fibrosi cistica in degenti ospedalieri), e Escherichia coli (intossicazione alimentare). Alcuni gammaproteobacteria sono ossidanti del metano.
I Gammaproteobacteria sono una classe di batteri, rilevante sia sotto il punto di vista medico che scientifico. Un certo numero di importanti batteri patogeni appartiene a questa classe, ad esempio la salmonella (responsabile di enteriti e febbri tifoidi), Yersinia pestis (agente patogeno della peste), Vibrio cholerae (vibrione che provoca il colera), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (infezioni polmonari e fibrosi cistica in degenti ospedalieri), e Escherichia coli (intossicazione alimentare). Alcuni gammaproteobacteria sono ossidanti del metano.
Gammaproteobacteria – proteobakterijų (Proteobacteria) tipo bakterijų klasė.
Gammaproteobacteria – proteobakterijų (Proteobacteria) tipo bakterijų klasė.
Gammaproteobacteria is een klasse van medisch en wetenschappelijk belangrijke bacteriën. Tot de klasse behoren onder andere de Enterobacteriaceae (bijvoorbeeld Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae en Pseudomonadaceae. Enkele bekende voorbeelden van humane pathogenen die tot deze klasse behoren zijn: Salmonella (voedselinfecties), Yersinia (de pest), Vibrio cholerae (cholera), Escherichia coli (voedselvergiftiging) en Pseudomonas aeruginosa (longinfecties bij patiënten met mucovisidose). Alle proteobacteria, en dus ook de gammaproteobacteria zijn gram-negatief.
Er zijn gammaproteobacteria die in staat zijn om aan fotosynthese te doen en oxideren waterstofsulfide (in plaats van water), waardoor ze zwavel in intracellulaire granules opstapelen. Sommige gammaproteobacteria oxideren methaan of metalen.
Gammaproteobacteria is een klasse van medisch en wetenschappelijk belangrijke bacteriën. Tot de klasse behoren onder andere de Enterobacteriaceae (bijvoorbeeld Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae en Pseudomonadaceae. Enkele bekende voorbeelden van humane pathogenen die tot deze klasse behoren zijn: Salmonella (voedselinfecties), Yersinia (de pest), Vibrio cholerae (cholera), Escherichia coli (voedselvergiftiging) en Pseudomonas aeruginosa (longinfecties bij patiënten met mucovisidose). Alle proteobacteria, en dus ook de gammaproteobacteria zijn gram-negatief.
Gammaproteobacteria – klasa bakterii z typu proteobakterii[1].
Gammaproteobacteria – klasa bakterii z typu proteobakterii.
Gammaproteobacteria (do grego gamma, terceira letra do alfabeto grego; + Proteus, deus do oceano capaz de mudar de forma; + bakterion, pequeno bastão; + ia, sufixo que indica classe) é uma classe de bactérias gram-negativas do filo Proteobacteria. A classe é baseada na análise filogenética de seqüências de 16S rRNA, e todos os membros são relacionados com a ordem-tipo Pseudomonadales.[1]
A classe possui vários grupos de bactérias de importância médica e científica, como as famílias Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae e Pseudomonadaceae. Um grande número de agentes patogênicos para o homem e animais integram a classe, entre eles, Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp., Yersinia pestis, Vibrio cholerae e Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Gammaproteobacteria (do grego gamma, terceira letra do alfabeto grego; + Proteus, deus do oceano capaz de mudar de forma; + bakterion, pequeno bastão; + ia, sufixo que indica classe) é uma classe de bactérias gram-negativas do filo Proteobacteria. A classe é baseada na análise filogenética de seqüências de 16S rRNA, e todos os membros são relacionados com a ordem-tipo Pseudomonadales.
A classe possui vários grupos de bactérias de importância médica e científica, como as famílias Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae e Pseudomonadaceae. Um grande número de agentes patogênicos para o homem e animais integram a classe, entre eles, Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp., Yersinia pestis, Vibrio cholerae e Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Гамма-протеобактерії (γ Proteobacteria або Gammaproteobacteria) — клас бактерій типу протеобектерій.
Клас містить кілька важливих з медичної та наукової точки зору груп бактерій, таких як Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae і Pseudomonadaceae. До класу належить велике число важливих патогенів, наприклад Salmonella (викликає ентерит і черевний тиф), Yersinia (чума), Vibrio (холера), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (інфекції легенів у пацієнтів з імунодефіцитом або хворих на кістозний фіброз).
Гамма-протеобактерії (γ Proteobacteria або Gammaproteobacteria) — клас бактерій типу протеобектерій.
Клас містить кілька важливих з медичної та наукової точки зору груп бактерій, таких як Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli), Vibrionaceae і Pseudomonadaceae. До класу належить велике число важливих патогенів, наприклад Salmonella (викликає ентерит і черевний тиф), Yersinia (чума), Vibrio (холера), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (інфекції легенів у пацієнтів з імунодефіцитом або хворих на кістозний фіброз).
Gammaproteobacteria Garrity et al. 2005
ПорядкиГамма-протеобактерии (лат. Gammaproteobacteria) — класс грамотрицательных бактерий типа протеобактерий, в который входят некоторые группы, важные в медицинском, экологическом и научном плане. Сюда же относят чрезвычайно большое количество патогенных микроорганизмов.
К гамма-протеобактериям относятся несколько важных для медицины и биологии групп, таких как Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrionaceae и Pseudomonadaceae. К этому же классу принадлежат возбудители опасных заболеваний человека, например Salmonella spp. (энтерит и брюшной тиф), Yersinia pestis (чума), Vibrio cholerae (холера), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (заражение лёгких у госпитализированных пациентов или больных муковисцидозом), и Escherichia coli (пищевое отравление). Также к гамма-протеобактериям принадлежат патогены растений, например Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (рак цитрусовых) и Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae (поражает киви). Члены рода Chromatium способны к фотосинтезу с использованием сероводорода в качестве донора электронов, и, таким образом, участвуют в круговороте серы. Некоторые гамма-протеобактерии способны окислять метан, и многие из них вступают в симбиотические отношения с придонными обитателями океанических геотермальных источников[1].
Из-за единственного рода, Acidithiobacillus, класс гамма-протеобактерии оказался парафилетическим по отношению к бета-протеобактериям (см. Таксономия протеобактерий).
Phylogeny of GammaproteobacteriaRuthia, Vesicomyosocius, Thiomicrospira, Dichelobacter, Francisella
Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Alteromonas, Idiomarinaceae
На май 2015 года класс Gammaproteobacteria содержит следующие порядки и семейства[3]:
Гамма-протеобактерии (лат. Gammaproteobacteria) — класс грамотрицательных бактерий типа протеобактерий, в который входят некоторые группы, важные в медицинском, экологическом и научном плане. Сюда же относят чрезвычайно большое количество патогенных микроорганизмов.
目
詳見細菌分類表
γ‐變形菌綱是目前所知的細菌中種類最多的一綱,包括一些醫學上和科學研究中很重要的類群,如腸桿菌科(Enterobacteraceae)、弧菌科(Vibrionaceae)和假單胞菌科(Pseudomonadaceae)。很多重要的病原菌屬於這個綱,如沙門氏菌屬(Salmonella)(腸炎和傷寒)、耶爾辛氏菌屬(Yersinia)(鼠疫)、弧菌屬(Vibrio)(霍亂)、綠膿桿菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)(就醫時引發的肺部感染或者囊性纖維化)。重要的模式生物大腸桿菌也屬於此綱。
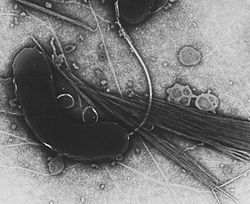
ガンマプロテオバクテリア綱(Gammaproteobacteria)とは真性細菌プロテオバクテリア門における綱の一つである。この綱の細菌はグラム陰性である。重要な病原菌を多く含む。
ガンマプロテオバクテリア綱には医学的、社会的に重要な細菌を多く含む。腸内細菌科(Enterobacteriaceae)、ビブリオ科(Vibrionaceae)、シュードモナス科(Pseudomonadaceae)などである。重要な病原菌にはSalmonella spp.(腸炎や腸チフスの原因菌)やYersinia pestis(ペスト)、Vibrio cholerae(コレラ)Pseudomonas aeruginosa(日和見感染による緑膿菌感染症)、Escherichia coli(食中毒)がいる。重要な植物病原菌にはXanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri(ミカン類潰瘍病)やPseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae(キウイ)、Xylella fastidiosaがいる。クロマチウム属(Chromatium)は光合成細菌であり、水の代わりに硫化水素を酸化し、硫黄を排出する。ガンマプロテオバクテリア綱の多くはメタン酸化細菌であり、一部は深海生物のチューブワームと共生している[1]。
Ruthia, Vesicomyosocius, Thiomicrospira, Dichelobacter, Francisella
Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Alteromonas, Idiomarinaceae
ガンマプロテオバクテリア綱はベータプロテオバクテリア綱の側縁である。以下の属は、帰属させる目と科がいまだ不明である。Alkalimarinus属、Alkalimonas属、Arenicella属、Gallaecimonas属、Ignatzschineria属、Litorivivens属、Marinicella属、Methylohalomonas属、Methylonatrum属、Plasticicumulans属、Pseudohongiella属、Sedimenticola属、Thiohalobacter属、Thiohalomonas属、Thiohalorhabdus属、Thiolapillus属およびWohlfahrtiimonas属[3]。
ガンマプロテオバクテリア綱(Gammaproteobacteria)とは真性細菌プロテオバクテリア門における綱の一つである。この綱の細菌はグラム陰性である。重要な病原菌を多く含む。
감마프로테오박테리아(Gammaproteobacteria)는 프로테오박테리아문에 속하는 세균 강의 하나이다. 엔테로박테리아과(Escherichia coli), 비브리오과, 극모세균과 등과 같은 의학적, 환경적, 과학적으로 매우 중요한 세균을 포함하고 있다.
예를 들어, 이 세균 강에는 살모넬라속(장염과 장티푸스), 예르시니아속(페스트), 비브리오속(콜레라), 녹농균(병원 환자 또는 성 섬유증 환자에게 폐감염을 일으키는 원인균), 폐렴을 일으키는 폐렴막대균(Klebsiella pneumoniae) 등 많은 수의 병원성 세균이 속해 있다. 다른 모든 프로테오박테리아처럼 그람-음성균이다.
감마프로테오박테리아(Gammaproteobacteria)는 프로테오박테리아문에 속하는 세균 강의 하나이다. 엔테로박테리아과(Escherichia coli), 비브리오과, 극모세균과 등과 같은 의학적, 환경적, 과학적으로 매우 중요한 세균을 포함하고 있다.
예를 들어, 이 세균 강에는 살모넬라속(장염과 장티푸스), 예르시니아속(페스트), 비브리오속(콜레라), 녹농균(병원 환자 또는 성 섬유증 환자에게 폐감염을 일으키는 원인균), 폐렴을 일으키는 폐렴막대균(Klebsiella pneumoniae) 등 많은 수의 병원성 세균이 속해 있다. 다른 모든 프로테오박테리아처럼 그람-음성균이다.