en
names in breadcrumbs


The origin of the Malagasy mammalian fauna is a complicated mystery, mainly because of the island's poor Tertiary fossil record. The island of Madagascar has been surrounded by ocean for approximately 88 million years, which predates the age of origin for the four orders of terrestrial mammals existing on Madagascar today (carnivorans, primates, rodents and lipotyphlan insectivores).
A multigene analysis was used to determine if Malagasy carnivorans are all descendents of a single African ancestor: the product of a single colonization of the island. Results provide support for this single colonization theory. Also supported is that this single common ancestor was of herpestid form. However, there are two Malagasy felids residing within the herpestid clade. Malagasy carnivores could be of a feliform lineage, which can be classed with the viverrids, but they do not belong to a monophyletic Viverridae, and some subsets of Malagasy taxa are not classed within Herpestidae or Felidae.
The difficulty in comparing G. fasciata with other herpestids is that even though traditional family affiliations are given, they do not reflect phylogenetic relationships. DNA comparative analyses can help determine whether the broad-striped mongooses can be compared to other herpestids. More information is needed on these mongooses to do comparisons.
It is not known whether G. fasciata is preyed upon or not.
Broad-striped mongooses have nimble, low to the ground bodies. They are small to medium in size, comparable to American martens. They have short legs and long bushy tails. Their heads are long, slender and dorso-ventrally flattened with a pointed rostrum. Broad-striped mongooses may be confused with the introduced carnivore Viverricula indica which has similar coloration.
Galidictis fasciata can be identified by its distinctive grey-beige pelage extending to the under-belly. The body has about five longitudinal dark brown or black stripes that are broader than the creamy-beige spaces separating them, and continue from the nape dorsally to about one third the length of the tail. The top of the head is darker than the cheeks, chin and throat. The very distinctive tails are a creamy white. Ears are small and are covered with short, fine fur. The only other species of Galidictis, Galadictis grandidieri, has dark stipes which are narrower than the lighter spaces; the outermost portion of the ear lacks fur.
Various sources list weights between 500 and 800 grams, with a mean adult body mass of 605 grams. Length of head and body is 320 to 340 mm and tail length is 280 to 300 mm. Females are slightly smaller and lighter than males. Feet have longer digits, longer claws, and less webbing than other herpestids.
Range mass: 380 to 800 g.
Average mass: 605 g.
Range length: 550 to 640 mm.
Average length: 570 mm.
Other Physical Features: endothermic ; homoiothermic; bilateral symmetry
Sexual Dimorphism: male larger
Although accounts do exist of Galidictis species in captivity, these do not incorporate data from any extended period of time. Otherwise, little is known about the lifespan of broad-striped mongooses. Other Malagasy mongooses kept in captivity show a great variation in lifespan. A Malagasy ring-tailed mongoose is reported to have lived over 24 years in captivity. However, a Malagasy brown-tailed mongoose is reported to have lived only 4 years and 9 months. It is not known where in this spectrum of variation Galidictis species fall.
Observations of the distribution of G. fasciata range from 440 meters to approximately 1500 meters elevation, from lowland to montane forest. Although mostly terrestrial, broad-striped mongooses have been observed climbing in trees, and on large, fallen logs.
Range elevation: 440 to 1500 m.
Average elevation: 810 m.
Habitat Regions: tropical ; terrestrial
Terrestrial Biomes: forest ; rainforest ; mountains
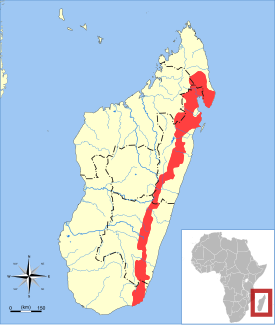
Broad-striped mongooses are found only in the eastern rainforests of Madagascar. These mongooses have been reported from the Mananara-Nord region in the north to the Réserve Naturelle Intégrale (RNI) d'Andohahela in the south. Other than second-hand reports, there is currently no firm evidence of Galidictis fasciata distribution further north than the Marojejy Massif, which is south of the Masoala Peninsula located in the extreme northeastern portion of the island.
Biogeographic Regions: ethiopian (Native )
Other Geographic Terms: island endemic
It has been surmised that broad-striped mongooses feed largely on rodents, small lemurs, and even reptiles and amphibians. There isn't any strong evidence of G. fasciata eating lemurs. Also, it is suggested that they feed on invertebrates. Field studies of tropical forest carnivores may be difficult because of their nocturnal, often solitary habits, and difficulty in luring them into traps.
Animal Foods: mammals; amphibians; insects
Primary Diet: carnivore (Eats terrestrial vertebrates)
Because this species is so poorly studied, it is difficult to determine what role it plays within its ecosystem. As a predator, G. fasciata probably has some impact on prey populations. It may compete with other small carnivores, but details of such interactions are lacking.
No information is available on the positive economic importance G. fasciata has for humans.
There are no known adverse affects of G. fasciata on humans.
At this time, it is unknown how broad-striped mongooses communicate or perceive the environment. As mammals, it is likely that they use some combination of tactile, visual, chemical, and accoustic cues in dealing both with their environment and with each other.
Communication Channels: visual ; tactile ; acoustic ; chemical
Perception Channels: visual ; tactile ; acoustic ; chemical
The IUCN currently lists G. fasciata as vunerable. Human advancement into the forests, logging, and clearing are decreasing habitat. There is competition for resources, mainly dietary, from small Indian civets, Viverricula indica, as well as from feral cats and dogs, all of which have been introduced.
US Federal List: no special status
CITES: no special status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: near threatened
Currently, knowledge is lacking about the reproductive activities of G. fasciata. Garbutt (1999) suggests that these rarely seen animals are probably pair bonded, and so are likely to be monogamous. The lack of highly developed sexual dimorphism supports this possible mating system.
Seasonality and reproductive activity of G. fasciata and its close relative G. grandidieri are currently not known. A female captured in November did not show reproductive characteristics. It has been determined that the maximum number of mammae is two. Males captured in October and late November did have scrotal testes volume of 1884 mm. This species has been observed to have a maximum litter size of one.
Other herpestids found on Madagascar may provide some clues about the reproduction of this rarely seen mammal. Malagasy ring-tailed mongooses breed seasonally, from April until November. Young are born between July and February, after a gestation of 79 to 92 days. Conversely, Malagasy narrow-striped mongooses breed from December to April, with mating peaking in the Malagasy summer months of February and March. These mongooses have a slightly longer gestation period, reported as 90 to 105 days. Both of these herspestid species typically give birth to a single young. In the latter species, the young is weaned at about 2 months of age. In both species, the young appear to reach sexual maturity around 2 years of age, and have an extended association with parents. Galidictis fasciata is probably similar to the other Malagasy herpestids in these characteristics, but more research is needed to know for sure.
Breeding interval: There animals probably breed annually.
Breeding season: The breeding season of Galidictis fasciata is not known.
Range number of offspring: 1 (high) .
Key Reproductive Features: iteroparous ; gonochoric/gonochoristic/dioecious (sexes separate); sexual ; fertilization ; viviparous
Nothing is known about parental investment of G. fasciata. Depite paucity of data, we can reasonably infer that females care for the young, providing them with shelter, milk, and protection at least until the time of weaning. If G. fasciata is like other Malagasy herpestids, specifically Mungotictis decemlineata, the young may remain with the mother until sexually mature, around the age of 2 years. The role of males in parental care is not known, and further research is needed to clarify the exact relationship between the mother and her young.
Parental Investment: altricial ; pre-fertilization (Provisioning, Protecting: Female); pre-hatching/birth (Provisioning: Female, Protecting: Female); pre-weaning/fledging (Provisioning: Female, Protecting: Female); pre-independence (Protecting: Female)
Ar vibinell roudennoù ledan (Galidictis fasciata) a zo ur bronneg kigdebrer eus kerentiad an Eupleridae.
He c'havout a reer e koadegoù reter Madagaskar. Anavezout a reer daou isspesad G. f. striata ha G. F. fasciata disheñvelaet dre stumm o lost ha niver o roudennoù.
Un aneval-noz eo. Hemolc'hiñ a ra krignerien bihan. Bevañ a ra e koubladoù. Ur c'holen a vez ganet bep bloaz.
Ar vibinell roudennoù ledan (Galidictis fasciata) a zo ur bronneg kigdebrer eus kerentiad an Eupleridae.
He c'havout a reer e koadegoù reter Madagaskar. Anavezout a reer daou isspesad G. f. striata ha G. F. fasciata disheñvelaet dre stumm o lost ha niver o roudennoù.
Un aneval-noz eo. Hemolc'hiñ a ra krignerien bihan. Bevañ a ra e koubladoù. Ur c'holen a vez ganet bep bloaz.
La mangosta de bandes amples (Galidictis fasciata), és una espècie de mangosta de la família dels euplèrids.
La mangosta de bandes amples té un cos baix i àgil i és de mida petita o mitjana, comparable a l marta nord-americana. Té les potes curtes, una cua llarga i espessa i un cap llarg i aplanat amb un rostre puntegut. A causa de la coloració similar, sovint es poden confondre amb la introduïda civeta petita de l'Índia.[1][2]
La mangosta de bandes amples es pot identificar pel seu pelatge gris-beix distintiu s'estén fins al ventre. El cos té uns cinc bandes longitudinals de color marró fosc o negre que són més amples que els espais de color beix-crema que les separa i que van des del clatell fins a la cua. La part superior del cap és més fosca que les galtes, la barbeta i la gola. Les cues són d'un color blanc cremós molt distintiu. Les orelles són petites i estan cobertes de pèl curt i fi. L'altra espècie del gènere Galidictis, la mangosta de Wozencraft, que també té bandes fosques, les té més estretes que els espais intermedis més clars i no té pèls a la part externa de les orelles.[3][1][2]
Alguns fonts indiquen pesos entre 500 i 800 grams, una longitud del cap i del cos entre 32 i 34 centímetres i una longitud de la cua entre 28 i 30 centímetres. Les femelles són una mica més petites i lleugeres que els mascles. La mangosta de bandes amples té els dits i les urpes més llargues que altres mangostes.[1][4]
Viuen a les selves de l'est de Madagascar. S'ha informat de la presència d'aquestes mangostes des de la regió de Mananara-Nord al nord, fins al Parc natural d'Andohahela al sud. Altres informes indiquen que actualment no hi proves de la que seva distribució es produeixi més al nord del massís de Marojejy Massif, el qual es troba al sud de la península de Masoala, situada a l'extrem nord-est de l'illa.[3][1][4][5][2]
Les observacions de la seva distribució s'han produït en alçades entre els 440 i els 1500 metres, tant en boscos de les terres baixes com en boscos de muntanya.[1][4]
La mangosta de bandes amples no ha estat estudiada exhaustivament. Això podria ser a causa dels seus hàbits estrictament nocturns. Malgrat ser animals terrestres, se les ha vist pujant als arbres o en troncs llargs caiguts. No obstant això, es desconeix on troben refugi.[3][1][4][2]
Com la majoria de mangostes de Madagascar, no són gaire socials. Sovint es troben sols o en petits grups familiars. Garbutt (1999) suggerí que podria tenir vincles de parella i per tant la seva sociabilitat es podria estendre a una parella i les seves cries. No obstant això, la mangosta de bandes estretes, s'ajunta per reproduir-se durant l'estiu de Madagascar. Durant l'hivern, s'ha informat que aquesta espècie format per unitat temporals, com poden ser parelles, grups maternals, o grups de mascles. La mangosta de bandes amples podria ser que formés grups com els d'aquesta altra mangosta. Tot i així, cal més investigacions per aclarir el comportament social d'aquesta espècie.[3][2]
S'ha conjecturat que s'alimenten principalment de rosegadors, petits lèmurs i fins i tot, de rèptils i amfibis. No ho proves determinants que s'alimenti de lèmurs. També s'ha suggerit que s'alimenta d'invertebrats. Els estudis sobre carnívors dels boscos tropicals es poden veure dificultats pels seus hàbits nocturns i sovint solitaris i per la dificultat d'atreure'ls a les trampes.[3][1][6][2]
Actualment, hi ha un desconeixement de les activitats reproductives de la mangosta de bandes amples. Garbutt (1999) suggereix que aquests animals rarament vistos, probablement tenen vincles de parella i per tant són monògams. La manca d'un dimorfisme sexual altament desenvolupat dóna suport a aquest sistema d'aparellament.[3][1][2]
La temporalitat i l'activitat d'aquesta espècie és actualment desconeguda. S'ha determinat que les femelles tenen dues mames i s'ha observat que aquesta espècie té ventrades d'una sola cria.[3][1][2]
Altres mangostes de Madagascar podrien donar pistes sobre la reproducció d'aquest mamífer tan difícil de veure. La mangosta de cua anellada es reprodueix estacionalment, de l'abril al novembre i les cries neixen entre juliol i febrer, després d'un període de gestació que varia entre 79 i 92 dies. En canvi, la mangosta de bandes estretes es reprodueix entre desembre i abril, amb un pic reproductiu durant l'estiu (de Madagascar) entre febrer i març i un període de gestació lleugerament més llarg, d'entre 90 i 105 dies. Aquestes dues espècies de mangosta donen a llum una única cria. En aquesta última espècie, el cadell és deslletat als voltants dels 2 mesos d'edat. En ambdues espècies, els joves sembla que assoleixen la maduresa sexual entorn dels 2 anys i tenen una llarga associació amb els pares. La mangosta de bandes amples té probablement trets semblants als de les altres mangostes de Madagascar, encara que cal més investigació per saber-ho amb seguretat.[2]
Es desconeix completament el procés de cria dels cadells de mangosta de bandes amples. Malgrat aquesta manca de dades, és raonable suposar que les mares crien els cadells, proporcionant-los refugi, llet i protecció, com a mínim fins al moment del deslletament. Si el seu comportament és com el d'altres mangostes de Madagascar, especialment com la mangosta de bandes estretes, els joves podrien romandre amb la mare fins a assolir la maduresa sexual als voltants dels 2 anys. Es desconeix el paper dels mascles en la cria dels cadells, per aquesta raó i per tractar d'aclarir la relació exacta entre la mare i la cria, calen més investigacions.[3][1][2]
Tot i que hi ha registres de les espècies del gènere Galidictis en captivitat, aquests no inclouen dades de cap període prolongat. En canvi, se sap poc sobre la vida útil de mangostes de bandes amples. Altres mangostes de Madagascar en captivitat mostren una esperança de vida molt variada. Una mangosta de cua anellada visqué més de 24 anys en captivitat, mentre que una mangosta bruna de Madagascar visqué només 4 anys i 9 mesos. Es desconeix l'encaix de la mangosta de bandes amples dins d'aquest espectre d'esperança de vida tant variable.[3][1][2]
Avui en dia, es desconeix com es comunica o percep l'entorn aquesta espècie. Com a mamífer, és probable que faci servir una combinació de senyals tàctils, visuals, químiques i acústiques, per relacionar-se amb l'entorn i altres individus.
La mangosta de bandes amples (Galidictis fasciata), és una espècie de mangosta de la família dels euplèrids.
Der Breitstreifenmungo (Galidictis fasciata) ist eine Raubtierart aus der Gruppe der Madagassischen Raubtiere (Eupleridae).
Breitstreifenmungos erreichen eine Kopfrumpflänge von 30 bis 34 Zentimetern, der Schwanz misst 25 bis 29 Zentimeter und das Gewicht beträgt 520 bis 750 Gramm. Ihr Körperbau ist schlank und langgestreckt, die Beine sind kurz. Namensgebendes Merkmal sind die graubraunen Längsstreifen, die durch weiße Streifen getrennt sind und sich am Rücken vom Nacken bis zur Schwanzwurzel erstrecken. Der Bauch ist hellgrau, das Gesicht ist graubraun gefärbt. Der Schwanz ist buschig, die hinteren zwei Drittel sind auffallend weiß.
Diese Raubtiere sind auf Madagaskar endemisch, wo sie die Regenwälder entlang der gesamten Ostküste bewohnen. Sie leben meist unter 700 Höhenmetern, können aber bis in 1500 Meter Seehöhe vorkommen. Die meisten Funde stammen aus intakten Wäldern, es gibt jedoch auch Berichte über Vorkommen der Art in teilweise abgeholzten Gebieten.
Über die Lebensweise der Breitstreifenmungos ist wenig bekannt. Sie sind nachtaktiv und halten sich meist am Boden auf, können aber auch auf Bäume klettern. Die meisten Beobachtungen sprechen für eine einzelgängerische Lebensweise oder für ein Leben in Paaren. Ihre Nahrung besteht wahrscheinlich aus Nagetieren, kleinen Lemuren sowie diversen Reptilien und Amphibien.
Breitstreifenmungos leben in geringen Populationsdichten und werden selten beobachtet, allerdings dürfte ihr Verbreitungsgebiet relativ groß sein. Gebietsweise leiden sie an der Zerstörung ihres Lebensraums, auch die Konkurrenz durch die eingeschleppte Kleine Indische Zibetkatze eine Gefahr darstellen. Die IUCN listet die Art als „gering gefährdet“ (near threatened).
Der Breitstreifenmungo (Galidictis fasciata) ist eine Raubtierart aus der Gruppe der Madagassischen Raubtiere (Eupleridae).
Galidictis fasciata es un specie de Galidictis.
Galidictis fasciata — від клясы сысуноў атрада драпежных сямейства Eupleridae.
The broad-striped Malagasy mongoose or broad-striped vontsira (Galidictis fasciata) is a species of Galidiinae, a subfamily of mongoose-like euplerids native to Madagascar. The species contains two known subspecies: Galidictis fasciata fasciata and Galidictis fasciata striata.[1]
Their main distinguishing factors are their stripes and their tails; G. f. fasciata has a fuller, reddish-brown tail and 8-10 stripes, while G. f. striata has a thinner, white tail and 5 stripes. They are all forest-dweller on the eastern side of the island, and their primary prey is small rodents. This species is most active in the evening and at night.
The specific epithet fasciata means ‘banded’ in Latin. Its local common name is vontsira fotsy, ‘white vontsira’ in Malagasy.[3]
The broad-striped Malagasy mongoose or broad-striped vontsira (Galidictis fasciata) is a species of Galidiinae, a subfamily of mongoose-like euplerids native to Madagascar. The species contains two known subspecies: Galidictis fasciata fasciata and Galidictis fasciata striata.
Their main distinguishing factors are their stripes and their tails; G. f. fasciata has a fuller, reddish-brown tail and 8-10 stripes, while G. f. striata has a thinner, white tail and 5 stripes. They are all forest-dweller on the eastern side of the island, and their primary prey is small rodents. This species is most active in the evening and at night.
The specific epithet fasciata means ‘banded’ in Latin. Its local common name is vontsira fotsy, ‘white vontsira’ in Malagasy.
La mangosta de franjas anchas, (Galidictis fasciata), es una especie de mamífero carnívoro de la familia Galidictis. Es un habitante del bosque del oriente de Madagascar. Esta especie está conformada por dos subespecies: G. f. striata and G. f. fasciata. Sus características distintivas son sus rayas y su cola; la primera especie tiene una cola delgada y blanca y cinco franjas tripes, mientras la segunda tiene una cola gruesa de color marrón rojizo y de ocho a diez franjas. Esta especie se alimenta de roedores pequeños. Esta especie es más activa en la tarde que en la noche. Viven en parejas y se reproducen anualmente, obteniendo una cría cada temporada seca.
La mangosta de franjas anchas, (Galidictis fasciata), es una especie de mamífero carnívoro de la familia Galidictis. Es un habitante del bosque del oriente de Madagascar. Esta especie está conformada por dos subespecies: G. f. striata and G. f. fasciata. Sus características distintivas son sus rayas y su cola; la primera especie tiene una cola delgada y blanca y cinco franjas tripes, mientras la segunda tiene una cola gruesa de color marrón rojizo y de ocho a diez franjas. Esta especie se alimenta de roedores pequeños. Esta especie es más activa en la tarde que en la noche. Viven en parejas y se reproducen anualmente, obteniendo una cría cada temporada seca.
Galidictis fasciata Galidictis generoko animalia da. Artiodaktiloen barruko Galidiinae azpifamilia eta Eupleridae familian sailkatuta dago.
Galidictis fasciata Galidictis generoko animalia da. Artiodaktiloen barruko Galidiinae azpifamilia eta Eupleridae familian sailkatuta dago.
Juovamangusti (Galidictis fasciata) on itäisellä Madagaskarilla elävä madagaskarinmangusteihin kuuluva petoeläinlaji. Se on väriltään vaaleanruskea tai harmaa ja sillä on leveät, tummat raidat selässä ja kyljissä. Lajista tunnetaan kaksi alalajia G. f. striata ja G. F. fasciata. Ensin mainitulla on viisi raitaa ja valkoinen häntä, jälkimmäisellä on 8–10 raitaa ja pörröisempi punaruskea häntä.[2]
Juovamangusti (Galidictis fasciata) on itäisellä Madagaskarilla elävä madagaskarinmangusteihin kuuluva petoeläinlaji. Se on väriltään vaaleanruskea tai harmaa ja sillä on leveät, tummat raidat selässä ja kyljissä. Lajista tunnetaan kaksi alalajia G. f. striata ja G. F. fasciata. Ensin mainitulla on viisi raitaa ja valkoinen häntä, jälkimmäisellä on 8–10 raitaa ja pörröisempi punaruskea häntä.
Galidie à bandes, Galidie rayée
La Galidie à bandes ou Galidie rayée (Galidictis fasciata) est un mammifère carnivore appartenant à la famille des Eupleridae.
Cette espèce est endémique de Madagascar. Elle vit dans la forêt tropicale humide de basse altitude. Elle est apparemment limitée aux forêts ayant un sol latéritique[1].
Galidie à bandes, Galidie rayée
La Galidie à bandes ou Galidie rayée (Galidictis fasciata) est un mammifère carnivore appartenant à la famille des Eupleridae.
La mangusta fasciata (Galidictis fasciata (Gmelin, 1788)) è un carnivoro della famiglia degli Eupleridi[2].
Il colore di fondo del mantello è marroncino-crema; su di esso spiccano delle strisce longitudinali scure, che vanno dalle orecchie alla base della coda. Rispetto alle altre specie di manguste del Madagascar, ha zampe più lunghe e piedi più grandi. Maschi e femmine sono quasi indistinguibili; anche i giovani hanno lo stesso aspetto e si differenziano dagli adulti soltanto per le minori dimensioni.
Come tutte le specie della sua famiglia, è endemico del Madagascar, di cui abita le foreste orientali.
Mangia in prevalenza roditori e piccoli lemuri, ma anche rettili e anfibi.
Sappiamo molto poco su G. fasciata, poiché l'habitat forestale in cui vive rende molto difficile compiere studi approfonditi. Sappiamo tuttavia che è più attiva di sera e nel cuore della notte. Vive in coppie che si riproducono ogni anno, nei mesi estivi.
Viene suddiviso in due sottospecie: G. f. fasciata e G. f. striatus. Esse si distinguono tra loro per l'aspetto delle strisce e della coda. La prima ha la coda bianca e sottile e cinque strisce, mentre la seconda ha la coda marrone-rossiccia e spessa e otto-dieci strisce.
Come tutte le specie della sua famiglia, si è evoluto indipendentemente da tutti gli altri Carnivori sull'isola di Madagascar, separatasi dal continente africano già dagli inizi dell'era cenozoica. In passato veniva classificato tra le manguste, nella famiglia degli Erpestidi, ma recenti studi di biologia molecolare ne hanno sottolineato la stretta parentela con altri carnivori malgasci.
La mangusta fasciata (Galidictis fasciata (Gmelin, 1788)) è un carnivoro della famiglia degli Eupleridi.
De vijfstreepmangoest (Galidictis fasciata) is een roofdier uit de familie van madagaskarcivetkatten (Eupleridae). Ze leven in de regenwouden van Madagaskar, vooral op 440 m tot 1500 m hoogte. Ze worden ongeveer 32 tot 34 cm lang met een staart van 28 tot 30 cm en wegen tussen de 500 en 800 gram. Ze hebben zoals hun naam al zegt 5 donkerbruin tot zwarte strepen op hun lichaam.
Bronnen, noten en/of referentiesPasówka malgaska[3], paskówka malgaska (Galidictis fasciata) – gatunek drapieżnego ssaka z rodziny falanrukowatych (Eupleridae) wcześniej zaliczany do mangustowatych (Herpestidae).
Gatunek endemiczny wschodniego Madagaskaru. Występuje w lasach deszczowych.
Niewielki ssak o wydłużonym ciele z długim, grubym ogonem i krótkimi łapami. Ubarwienie szarobeżowe z czarnymi lub ciemnobrązowymi pasami ciągnącymi się wzdłuż boków ciała. Ogon kremowobiały.
Długość ciała 32-34 cm, długość ogona 28-30 cm. Przeciętna masa ciała nie przekracza 0,8 kg.
Paskówka malgaska jest gatunkiem rzadko spotykanym i słabo poznanym. Prowadzi nocny tryb życia, co utrudnia jej obserwację. Niewiele wiadomo na temat biologii rozrodu, preferencji żywieniowych i zachowań socjalnych tego gatunku.
Pasówka malgaska, paskówka malgaska (Galidictis fasciata) – gatunek drapieżnego ssaka z rodziny falanrukowatych (Eupleridae) wcześniej zaliczany do mangustowatych (Herpestidae).
Bredstrimmig mangust (Galidictis fasciata[2][3][4][5]) är en däggdjursart som först beskrevs av Gmelin 1788. Galidictis fasciata ingår i släktet Galidictis, och familjen Eupleridae.[6][7]
Djuret påminner om en mård men det finns inget nära släktskap mellan arterna. Extremiteterna är hos bredstrimmig mangust korta och svansen är lång och yvig. På Madagaskar kan arten förväxlas med liten indisk sibetkatt (Viverricula indica) som blev introducerad av människor. De kan skiljas åt med hjälp av svansens färgteckning som är enfärgat krämvit hos bredstrimmig mangust och bandad hos indisk sibetkatt. Övrig kropp är hos bredstrimmig mangust grå med gula skuggor och på ryggen finns upp till fem breda längsgående strimmor i svart eller mörkbrun.[8]
Kroppslängden (huvud och bål) ligger mellan 32 och 34 cm och svanslängden mellan 28 och 30 cm. Vikten är vanligen omkring 600 gram men kan variera mellan 380 och 800 gram.[8]
Arten förekommer på östra Madagaskar. Den vistas där i kulliga områden och upp till 1500 meter höga bergstrakter. Regionen är främst täckt av tropisk regnskog men djuret vistas även utanför skogen.[1]
Bredstrimmig mangust är bara aktiv på natten. Var den vilar på dagen är inte dokumenterad. Arten vistas främst på marken men kan klättra i växtligheten.[8] Individerna lever utanför parningstiden ensam eller i små grupper (vanligen under vintern). Födan utgörs huvudsakligen av små gnagare. Ibland äter bredstrimmig mangust mindre lemurer, kräldjur och groddjur samt i sällsynta fall ryggradslösa djur.[8] Troligen kan den jaga byten som är större än den själv.[1]
Det antas att fortplantningen sker under sommaren. Dräktigheten varar hos närbesläktade arter 80 till 105 dagar och troligen finns för bredstrimmig mangust liknande värden. Per kull föds bara en unge.[8]
Arten hotas huvudsakligen av habitatförstörelse genom skogsavverkningar och svedjebruk. Ett mindre hot är introducerade fiender eller konkurrenter som hundar, katter och liten indisk sibetkatt. IUCN kategoriserar arten globalt som nära hotad.[1]
Arten delas in i följande underarter:[6]
Bredstrimmig mangust (Galidictis fasciata) är en däggdjursart som först beskrevs av Gmelin 1788. Galidictis fasciata ingår i släktet Galidictis, och familjen Eupleridae.
Cầy mangut sọc rộng là một loài động vật có vú trong họ Eupleridae, bộ Ăn thịt. Loài này được Gmelin mô tả năm 1788.[2] Đây là loài động vật ăn thịt đặc hữu của Madagaxca.[1][3]
Cầy mangut sọc rộng là loài động vật nhanh nhẹn, có kích thước từ nhỏ đến trung bình. Chúng có đôi chân ngắn và cái đuôi dài rậm rạp, cái đầu dài, nhỏ và cái mõm nhọn. Bàn chân có móng vuốt dài hơn so với các loài cầy khác.[4]
Cầy mangut sọc rộng có đặc trưng bởi lớp lông màu xám be phủ tận đến dưới bụng. Trên cơ thể của chúng có khoảng năm sọc rộng màu nâu hoặc đen dọc theo cơ thể. Đỉnh đầu có màu đậm hơn má, cằm và cổ họng. Đặc biệt là đuôi có màu trắng kem. Tai nhỏ và được bao phủ bởi lông ngắn, mịn.[4]
Khối lượng của Cầy mangut sọc rộng từ 380 đến 800 gram, trung bình là 605 gram. Chiều dài đầu và thân là 320–340 mm và chiều dài đuôi là 280–300 mm. Con cái có hơi nhỏ hơn và nhẹ hơn so với con đực.[4][5]
Cầy mangut sọc rộng chỉ được tìm thấy trong rừng nhiệt đới phía đông của Madagascar, ở độ cao 440 m đến 1500 m so với mực nước biển, từ rừng thấp cho tới rừng trên núi.[4] Phạm vi phân bố của chúng trải dài từ phía bắc xuống phía nam nhưng mật độ thấp.[1]
Cầy mangut sọc rộng sống chủ yếu trên mặt đất[4] nhưng cũng quan sát thấy ở trên cây. Chúng sinh hoạt về đêm, với lối sống ít xã hội, có thể theo nhóm gia đình nhỏ. Con mồi của chúng được phỏng đoán là các loài động vật gặm nhấm, các loài vượn cáo nhỏ, và thậm chí cả bò sát, lưỡng cư và động vật không xương sống.[1]
Cầy mangut sọc rộng là một loài động vật có vú trong họ Eupleridae, bộ Ăn thịt. Loài này được Gmelin mô tả năm 1788. Đây là loài động vật ăn thịt đặc hữu của Madagaxca.
Galidictis fasciata
Gmelin, 1788
 Охранный статус
Охранный статус Широкополосый мунго[1] (лат. Galidictis fasciata) — хищное млекопитающее из семейства мадагаскарских виверр. Эндемик острова Мадагаскар, где он широко распространён в восточных влажных лесах от низин до высоты около 700 м над уровнем моря. Есть только одна запись наблюдения этого вида на высоте более 700 м (1500 м над уровнем моря). Плотность популяции низкая[2].
Ведёт ночной, в значительной степени наземный образ жизни[2].
Под угрозой разрушения находится среда проживания вида из-за лесозаготовки и преобразования леса в обрабатываемые земли. Вероятно, убивается собаками, сопровождающими охотников в лесу. Меньшую угрозу представляет конкуренция с одичавшими кошками, собаками и малой циветой (Viverricula indica). Проживает на нескольких природоохранных территориях[2].
Широкополосый мунго (лат. Galidictis fasciata) — хищное млекопитающее из семейства мадагаскарских виверр. Эндемик острова Мадагаскар, где он широко распространён в восточных влажных лесах от низин до высоты около 700 м над уровнем моря. Есть только одна запись наблюдения этого вида на высоте более 700 м (1500 м над уровнем моря). Плотность популяции низкая.
Ведёт ночной, в значительной степени наземный образ жизни.
Под угрозой разрушения находится среда проживания вида из-за лесозаготовки и преобразования леса в обрабатываемые земли. Вероятно, убивается собаками, сопровождающими охотников в лесу. Меньшую угрозу представляет конкуренция с одичавшими кошками, собаками и малой циветой (Viverricula indica). Проживает на нескольких природоохранных территориях.
 分類 界 : 動物界 Animalia 門 : 脊索動物門 Chordata 亜門 : 脊椎動物亜門 Vertebrata 綱 : 哺乳綱 Mammalia 目 : ネコ目 Carnivora 科 : マダガスカルマングース科 Herpestidae 亜科 : ワオマングース亜科 Galidiinae 属 : ヒロスジマングース属 Galisictis 種 : ヒロスジマングース
分類 界 : 動物界 Animalia 門 : 脊索動物門 Chordata 亜門 : 脊椎動物亜門 Vertebrata 綱 : 哺乳綱 Mammalia 目 : ネコ目 Carnivora 科 : マダガスカルマングース科 Herpestidae 亜科 : ワオマングース亜科 Galidiinae 属 : ヒロスジマングース属 Galisictis 種 : ヒロスジマングースヒロスジマングース(Galidictis fasciata)は、マダガスカルマングース科ヒロスジマングース属に分類される食肉類。
マダガスカル北東部[2]固有亜種
体長30-36センチメートル[3]。尾長24-30センチメートル[3]。体重0.5-0.6キログラム[3]。尾の体毛は房状に伸長する[2][3]。頸部から尾の基部にかけて幅広い縦縞が入る[1][2][3]。
指趾の間にはあまり発達しない水かきがある[2][3]。指趾は長く、爪も長い[2][3]。
乳頭の数は2個[3]。メスは生殖器の周辺(会陰腺)に臭腺がある[3]。
胴体の毛衣は淡褐色、腹面や尾の毛衣は白く尾基部は赤褐色[2]。縦縞は暗褐色で7本[2]。
胴体の毛衣は黄褐色で、腹面や四肢の毛衣は黄色、尾の毛衣は白い[2]。縦縞は暗赤褐色で8本[2]。
森林や湿原などに生息する[2][3]。夜行性および薄暮性[1][2][3]。ペアや小規模な群れを形成して生活する[1][2][3]。
食性は動物食で、小型哺乳類、昆虫、ミミズなどを食べる[3]。堆積物に口吻を差し入れ獲物を探す[3]。
開発による生息地の破壊などにより生息数は減少している[3]。
ヒロスジマングース(Galidictis fasciata)は、マダガスカルマングース科ヒロスジマングース属に分類される食肉類。
넓은띠몽구스(Galidictis fasciata)는 마다가스카르식육과 마다가스카르몽구스아과에 속하는 육식동물의 일종으로 마다가스카르 섬의 토착종이다. 띠몽구스속에 속하며 2종의 아종이 알려져 있다.[1] 두 아종의 구별되는 주요 특징은 줄무늬와 꼬리다. 파스키아타(G. f. fasciata)는 꼬리가 좀더 진한 불그스레한 갈색을 띠며 8~10개의 줄무늬가 있는 반면에, 스트리아타(G. f. striata)는 연한 흰색을 띠며 5개의 줄무늬가 있다. 모두 마다가스카르 섬 동부 지역 숲에서 서식하며, 주로 작은 설치류를 먹는다. 저녁과 밤에 가장 활발하게 생활한다. 종소명 "파스키아타"(fasciata)는 라틴어로 "줄무늬 모양의"(banded)라는 뜻이다. 현지에서는 "본시라 포시"(vontsira fotsy)로 불리며, 이는 말라가시어로 "흰색 본시라"(white vontsira)라는 의미이다.[3]
2종의 아종이 알려져 있다.[1]
다음은 마다가스카르식육과의 계통 분류이다.[4]
마다가스카르식육과 포사속† 자이언트포사
띠몽구스속 본시라속넓은띠몽구스(Galidictis fasciata)는 마다가스카르식육과 마다가스카르몽구스아과에 속하는 육식동물의 일종으로 마다가스카르 섬의 토착종이다. 띠몽구스속에 속하며 2종의 아종이 알려져 있다. 두 아종의 구별되는 주요 특징은 줄무늬와 꼬리다. 파스키아타(G. f. fasciata)는 꼬리가 좀더 진한 불그스레한 갈색을 띠며 8~10개의 줄무늬가 있는 반면에, 스트리아타(G. f. striata)는 연한 흰색을 띠며 5개의 줄무늬가 있다. 모두 마다가스카르 섬 동부 지역 숲에서 서식하며, 주로 작은 설치류를 먹는다. 저녁과 밤에 가장 활발하게 생활한다. 종소명 "파스키아타"(fasciata)는 라틴어로 "줄무늬 모양의"(banded)라는 뜻이다. 현지에서는 "본시라 포시"(vontsira fotsy)로 불리며, 이는 말라가시어로 "흰색 본시라"(white vontsira)라는 의미이다.