en
names in breadcrumbs


The capitula of P. capitatus support large communities of macrofauna dominated numerically by small crustaceans (mostly amphipods, tanaidaceans and large harpacticoid copepods). Stoner (1985) examined numbers of individuals, numbers of species, and species composition of crustaceans associated with P. capitatus of differing sizes during the dry and wet seasons in Puerto Rico. Abundance (number of individuals) and species richness (number of species) of crustaceans associated with P. capitatus increased with algal size. Faunal abundance rather than algal size, however, proved to be the best predictor of crustacean species richness on P. capitatus. Higher abundances of crustaceans (particularly amphipods and tanaidaceans) were found on P. capitatus than in the surrounding seagrass (Halodule wrightii) habitat.
Curtis et al. (2006) studied the use of P. capitatus and other algae by the the sacoglossan sea slug Elysia clarki. This sea slug feeds on siphonaceous algae and sequesters their chloroplasts within its cells, which actively photosynthesize for up to 4 months (E. clarki individuals starved for 4 months lose their chloroplasts and their color changes from green to yellow). Curtis et al. determined the algal source of chloroplasts in adults of E. clarki from the Florida Keys using molecular techniques, feeding experiments, and electron microscopy. They found that E. clarki sequester chloroplasts from at least four different species of algae, representing two genera: Penicillus lamourouxii, P. capitatus, Halimeda incrassata, and H. monile. Furthermore, they found that chloroplasts from more than one species of algae may be sequestered simultaneously in the same digestive cell.
Further investigations by Curtis et al. (2007) revealed that as they mature, E. clarki actually shift the algal species they consume and sequester chloroplasts from. In their experiments involving 29 algal species, the authors found that young juveniles ate only the thin filamentous species Bryopsis plumosa or Derbesia tenuissima. Transmission electron microscopy showed that the chloroplasts from both algae were sequestered intracellularly in juvenile slugs. Individuals offered any other macroalgae, including the four species fed on by adults, did not feed on or incorporate any chloroplasts, and soon died. Juveniles switched from consuming B. plumosa to P. capitatus at a length of ~1.0 cm, and when fixed for microscopy 14 days later had intact intracellular chloroplasts from both algae. The reason that juvenile E. clarki only feed on a few of the algal species utilized by adults is unknown, but mechanical issues are an obvious possibility. In the study by Clark et al. (2007), all of the algal species eaten by E. clarki are coenocytic. However,the authors note that P. capitatus, P. lamourouxii, H. incrassata, and H. monile are all calcareous algae, which may cause difficulties for the teeth of the juvenile radula in piercing the cell walls of the filaments. In addition, these four algae have fairly broad filaments. In contrast, B. plumosa and D. tenuissima are not calcified and have very fine filaments, which may be easier for the juvenile slug to grasp and perforate in order to suck out the cellular contents. However, juveniles did not feed on Vaucheria litorea, which is very similar morphologically to B. plumosa (fine filamentous and coenocytic), but is a chromophyte. Thus, filament size and shape alone does not determine feeding ability in E. clarki. The work by Clark et al. (2007) shows that E. clarki feeds on and sequesters chloroplasts from at least nine different species of green algae from four genera. None of the juvenile E. clarki fed on the algae preferred by adults (P. capitatus, P. lamourouxii, H. incrassata, and H. monile). Instead, the juveniles chose B. plumosa and D. tenuissima, and sequestered chloroplasts from those algal species. Adults in the field and in the lab will feed on Bryopsis spp. if it is available and sequester its chloroplasts.
In a study in two Caribbean bays, Wilson and Ramsook (2007) found that densities of epiphytic foraminifera on the capitulae (heads) of Penicillus capitatus were three times higher than those on either the alga Halimeda opuntia or on exposed seagrass (Manatee Grass, Syringodium filiforme; Turtle Grass ,Thalassia testudinum) rhizomes and basal leaves.
Penicillus capitatus is among the most common and conspicuous shallow water macroalgae in the Caribbean region. Individuals grow erect, up to about 15 cm tall, and are coenocytic, i.e., an individual consists of a single very large cell with many nuclei. The thallus (the "body" of the alga) is lightly calcified, giving it a whitish green color, except for the extreme tips of the filaments, which may be bright green. It consists of a stalk, anchored in sand or mud by a mass of rhizoids, and a terminal tuft of free filaments that are the source of its common (and scientific) name. (Hillson 1977; Abbott and Dawson 1978)
Penicillus capitatus is found in shallow subtidal waters throughout the Caribbean Sea, the Bahamas, Florida and Bermuda (Abbott and Dawson 1978; Taylor 1960, cited in Stoner 1985).
Penicillus capitatus is a common plant in warm, quiet waters of shallow bays and lagoons (Hillson 1977; Abbott and Dawson 1978).
The life span of Penicillus capitatus is about 45 days according to Wefer 1980 (cited in Wilson and Ramsook 2007).
Vadas et al. (1980) marked Penicillus pyriformis and P. capitatus in St. Croix and recorded ages ranging from 1 week to 16 weeks, with most individuals surviving 8 weeks or longer.
Penicillus capitatus has a long stalk and an oblong to spherical "brush" of filaments, which are the source of the common name Shaving Brush Alga. It is substantially calcified, with the stalk up to 10 cm long. The filamentous tufts are little more than 2 to 4 cm long. The individual filaments are very slender, but because of the calcification they are very tough. Under slight magnification, repeated branching of the filaments is apparent and the stalks appear spongy. Stalks are slightly constricted at the base, where the bulbous mass of rhizoids arises. (Hillson 1977)
Puglisi et al. (2004) isolated two new triterpene sulfate esters from Penicillus capitatus that are potent inhibitors of the well-known marine algal pathogen Lindra thallasiae.
In a study of nutrient limitation of P. capitatus found associated with seagrass meadows in Bermuda, McGlathery et al. (1992) concluded that growth of P. capitatus in their study area was limited by nitrogen availability. Algae species, such as P. capitatus, that are often found in oligotrophic (low-nutrient) water may be adapted to low nutrient conditions in the water column either through the ability to acquire nutrients directly from the sub-stratum and/or through "luxury uptake", i.e., when pulses of nutrients do become available, they are taken up and stored in excess of what is immediately needed. McGlathery et al. suggested that P. capitatus may acquire nutrients directly from sediment sources via rhizoid holdfasts.
Sexual reproduction in siphonous green algae (order Bryopsidales), including Penicillus, involves the release of anisogamous "male" and "female" gametes into the water column. (Anisogamy is the condition in which male and female gametes differ in size; isogamy describes the situation when they do not and there are no distinct male and female gametes, although there may still be different mating types.) In contrast to animals, the gametes of both sexes of many siphonous green algae (although not female gametes of Penicillus capitatus) are motile. Given that gametes are moving about in the water column and fertilization requires an encounter between a male and female gamete, gamete concentration is a critical factor determining fertilization success. This might be expected to favor the evolution of spawning synchrony between sexes within species, as in the mass spawning of numerous coral species, a phenomenon that was first described only in the early 1980s. Clifton did indeed find that synchronous, short-lived bouts of early moming spawning by tropical green algae is a widespread phenomenon on coral reefs. (Clifton 1997)
Clifton and Clifton (1999) reported further information about the spawning of Penicillus and other green algae in Caribbean Panama. For Penicillus, the time from onset of fertility to gamete release is about 48 hours. Penicillus exhibits a more extreme degree of anisogamy than do many other siphonous green algae, with macrogametes (female gametes) that are on the order of ten thousand times the size of the microgametes (male gametes). Although in Clifton and Clifton's study only a subset (generally about 5%) of the individuals of each species released gametes on a given morning, most species underwent bouts of sexual reproduction on numerous occasions during the seasonal peak of reproductive activity (March to May). As might be expected for holocarpic species (i.e., species that dedicate all their resources to reproductive tissue and die after a single grand bout of reproduction), dramatic declines in local algal abundance coincided with this period of maximal repriductive activity. The density of sand-dwelling genera such as Penicillus fell by 80 to 90% during March to May in 1997. Siphonous green seaweeds (Bryopsidales) are a ubiquitous and ecologically important feature of many tropical marine environments, including coral reefs, lagoons, mangrove swamps, and seagrass beds. Many calicified members of the Udoteacae (Halimeda, Penicillus, Rhipocephalus, and Udotea), commonly co-occur within these habitats, where their abundant biomass often makes them a significant source of food, shelter, competition, and calcium carbonate. (Clifton and Clifton 1999).
Clifton and Clifton found that unfertilized Penicillus gametes remained motile for 40 to 90 minutes, as determined by repetitive sampling of gametes released in buckets or aquaria. Males released their gametes several minutes before females, but there were no indications that this delay was due to chemical signaling or inducement by male gametes; remarkably, isolated females (placed in buckets the night before) released their gametes at the same time as other females on the reef. Fusion typically began occurring within minutes of gamete mixing and was observed up to 60 minutes after gamete release. All species studied were confirmed to be holocarpic, and bouts of sexual reproduction appeared to influence local abundance on reefs, as algal density and percentage cover dropped quickly during periods of peak reproduction. (Clifton and Clifton 1999)
The relatively inconspicuous onset of fertility in four species of Penicillus, including P. capitatus, was manifested by a whitening of the stipe as the cytoplasm migrated and a slight yellowing of the capitulum (the "brush") caused by the extension of uncalcified siphons (Meinesz 1980, cited in Clifton and Clifton 1989), occurred overnight, 48 to 60 hours before gamete release. The sex of individuals in these dioecious algae could be reliably identified 24 hours before gamete release. The capitulum of males was a distinctly lighter and greener color than the darker, grayer coloration of females. Males produced biflagellated microgametes similar in size and morphology to other genera; however, female Penicillus produced large (100 mm diameter) spheroid gametes with flagella arrayed along a membranous, sheetlike ‘‘tail’’. These negatively buoyant (i.e., tending to sink) gametes were non-motile and sank quickly despite flagellar motion that drove water past the gamete. The flagella were rapidly absorbed within 1 to 2 min of fertilization. Gamete release typically lasted 15 to 20 min, and resultant gamete clouds were inconspicuous. The dead thalli of post-reproductive Penicillus disappeared quickly in the field (often within 12 hours), especially the capitulum. This resulted both from disintegration of the thallus associated with water motion and from consumption by several specie sof parrotfish (Sparisoma aurefrenatum, S. chrysopterum, S. rubripinne, and S. viride). (Clifton and Clifton 1999)
Penicillus capitatus is a species of macroalgae, seaweed, that is part of the Udoteaceae, a larger family of algae.[1] The P. Capitatus is a member of green macroalgae, Chlorophyta, so they share some similarities to their terrestrial counterparts. Due to their distinct shape, the Penicillus genus can be referred to as Brush Seaweed, Shaving Brush, or the Mermaid's Shaving Brush.[2]
Penicillus capitatus is green in color, and vertically protrudes from the surface they grow on. It uses rhizoids, a type of root hair that aids in adhesion and the transport of water,[3] as a holdfast in order to stabilize itself on the surface that it is actively growing from.[4] Average lengths of the P. capitatus can vary; younger, smaller samples tend to be around 5 cm, while fully mature ones can be measured at 15 cm[5].
This species of macroalgae are capitate, which means that the longer stipe grows into a much wider capitulum. The diameter of the top can range from 5 to 8 centimeters.[6] This section of the seaweed contains smaller offshoots that make up the brush. The organism also produces calcium carbonate, however this only occurs along the cap and is absent from the stipe and other areas.[7] The calcium carbonate then creates a semi-hardened exterior on their cap and along the brush, which aids in providing shelter and nutrients to nearby organisms.[8]
P. capitatus is a coenocytic macroalgae.[9] Unlike other plants or various other forms of seaweed that have a cell wall around each and every cell, capitatus does not. Whenever the cells in this seaweed go through mitosis, there are no partitions between the cells formed, which means that the inside is a mixture of different nuclei as well as the separate organelles that were produced in each cell. This would then classify the Penicillus capitatus as a unicellular, multinucleated organism since there are no cell walls to make it multicellular.[10]
Due to the fact that Penicillus capitatus is a unicellular organism, this would mean that it is also siphonous.[11] Since cytokinesis does not occur during cell division, the stipe of these organisms has long tubes that go up to the very top of the macroalgae. These segments of the stem are lined with the cytosol and the organelles of the giant cell.[12]
The way that the Penicillus capitatus reproduces varies among each organism. The seaweed can reproduce asexually as well as sexually. Asexually, these organisms can reproduce by fragmentation.[13] This is done when the P. capitatus breaks into various little pieces and uses currents in order to disperse identical copies of themselves. Early sections of the stipe are produced closer to the bottom of the organism and are swiftly whisked away to grow in other areas. Sexually, the macroalgae can also reproduce by spreading gametes from non-calcified areas of the capitulum, although this has not been closely observed.[14]
The lifespan of the Penicillus capitatus has been under debate for quite some time. Some studies claim that an average life cycle can be as short as 45 days. On the other hand, opposing researchers concluded that on average the life cycle is 8 weeks, with some living for almost twice as long.[15]
The Penicillus capitatus was first observed by the Swedish botanist, Carl Linnaeus, in his publication dating back to 1758. His findings were recorded in the encyclopedia, Systema Naturae.[16] Unfortunately, the description of this organism was not as fully developed, and the subject was overlooked in the publication. However, at the beginning of the 19th century, there was a fair bit more attention put on fully describing and observing the macroalgae.
Naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck prominently recorded his findings regarding the P. capitatus. So much so that the lectotype name of the seaweed is Penecillus capitatus Lamarck.[17]
The term “Penicillus” is derived from the Latin word, "Penicillium”, which roughly translates to a "painter's brush".[18] Similarly to a painter's brush, the P. capitatus has a very thin stipe and shoots out upwards like the tufts on a brush. The latter half of the scientific name is derived from the Latin word “capitatus”, referring to the seaweed having a compressed head.[19] It was previously mentioned that a unique feature of the P. capitatus is that it is capitate, as it has a larger, compact top.
The Penicillus capitatus is found closer to the equator, in more tropical climates.[20] They are most abundant in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean. While not as common as in the Gulf and Caribbean, these organisms can be found on the Eastern Coast of South America. They have also been recorded in the Mediterranean (where Lamarck originally recorded his observations of the macroalgae) as well as on the eastern coast of Australia.[21]
The Penicillus capitatus develops in shallower, warmer water that is exposed to sunlight. This is due to them being thermophilic organisms, as they prefer to live in hotter areas.[22] These organisms have been found to be located in the neritic zones (very close to the shore) where the depths they comfortably reside in goes down to about 2 meters in depth.[23] While not much has been recorded regarding interactions with other facets of the ecosystem, Linnaeus' early recordings of the seaweed described it being a food source for sea turtles.[24]
These organisms are extremely important photosynthesizes in the estuary and lagoon environments.[25] P. capitatus are brackish[26] so they require very mild salinity in their habitat, so they only occur and thrive within these specific salinity levels throughout these areas. Within these areas, they spread to create meadows and ultimately provide many resources and shelter for the organisms around them.[27]
P. capitatus also occurs within mangrove forests and remains in very shallow waters.[28] In these habitats, the macroalgae tend to live with the local Thallasia, more commonly referred to as turtle grass. While not as common, they appear within coral reefs as well.[29]
The P. capitatus has been used across several academic studies and research papers throughout the latter half of the 20th century. One of the more significant experiments and papers arose from a 1985 study conducted by Allan Stoner. In this piece, he explored the relationships between the seaweed and various smaller organisms, like crabs, that would inhabit the sea brush, and how various factors affected the immigration rates of the creatures.[30] In 1992 Karen McGlarthy conducted experiments that connected P. capitatus’ decrease of nutrient uptake within various parts of Bermuda to be associated with the seagrass that inhabited the surrounding areas.[31] More recently, scientist in the Mediterranean studied how invasive species affect productivity and vitality of the macroalgae.[32]
Penicillus capitatus is a species of macroalgae, seaweed, that is part of the Udoteaceae, a larger family of algae. The P. Capitatus is a member of green macroalgae, Chlorophyta, so they share some similarities to their terrestrial counterparts. Due to their distinct shape, the Penicillus genus can be referred to as Brush Seaweed, Shaving Brush, or the Mermaid's Shaving Brush.
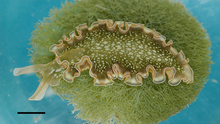
 Elysia clarki on its algal food source Penicillus capitatus. The scale bar is 5 mm.
Elysia clarki on its algal food source Penicillus capitatus. The scale bar is 5 mm.