en
names in breadcrumbs


Desmodium incanum, also known as creeping beggarweed, Spanish clover, Spanish tick-trefoil or hitchhikers is a perennial plant native to Central and South America.[1] In Hawaiʻi it is known as kaʻimi or kaimi clover from the Hawaiian for ("the seeker"). Initially introduced as forage crop around the world, it has spread to many places although it is no longer an important fodder crop. It is considered a weed both within and outside its native range.[1] It has spread through Florida and across the southern USA into southern Texas and across many Pacific islands, including Hawaii.
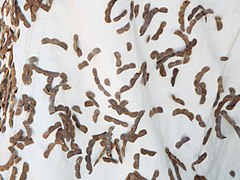
The plant has branched runners for reproduction. Its leaves are elliptic in shape and are hairy, and its flowers are pink to rose in color. Very frustrating in agriculture are its seedpods, which when ripe easily break off from the plant. They are also covered in sticky hairs (trichomes) that stick to any rough surface such as skin and hairs of animals and clothing thus aiding spreading. D. incanum is valuable for its ability to fix Nitrogen and thus increase soil fertility, thus it is commonly used as an intercrop.[1]
There has been long-standing confusion about the correct scientific name. This was long held to be Desmodium canum, and therefore for quite some time D. incanum was believed to be the correct name for the plant today called Desmodium laxiflorum.[2]
Desmodium incanum, also known as creeping beggarweed, Spanish clover, Spanish tick-trefoil or hitchhikers is a perennial plant native to Central and South America. In Hawaiʻi it is known as kaʻimi or kaimi clover from the Hawaiian for ("the seeker"). Initially introduced as forage crop around the world, it has spread to many places although it is no longer an important fodder crop. It is considered a weed both within and outside its native range. It has spread through Florida and across the southern USA into southern Texas and across many Pacific islands, including Hawaii.
The plant has branched runners for reproduction. Its leaves are elliptic in shape and are hairy, and its flowers are pink to rose in color. Very frustrating in agriculture are its seedpods, which when ripe easily break off from the plant. They are also covered in sticky hairs (trichomes) that stick to any rough surface such as skin and hairs of animals and clothing thus aiding spreading. D. incanum is valuable for its ability to fix Nitrogen and thus increase soil fertility, thus it is commonly used as an intercrop.
There has been long-standing confusion about the correct scientific name. This was long held to be Desmodium canum, and therefore for quite some time D. incanum was believed to be the correct name for the plant today called Desmodium laxiflorum.