Associations
(
англиски
)
добавил BioImages, the virtual fieldguide, UK
In Great Britain and/or Ireland:
Foodplant / feeds on
pycnidium of Diplodia coelomycetous anamorph of Diplodia siliquastri feeds on Cercis canadensis
Common Names
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
eastern redbud
redbud
Judas-tree
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Description
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
fruit,
shrub,
treeEastern redbud is a native, deciduous, small tree or shrub. Mature
height ranges from 25 to 50 feet (7.6-15.2 m); the smaller figure is
probably closer to average [
15,
16]. The crown is flat to rounded [
53].
The trunk us usually straight, branching about 5 to 9 feet (1.5-2 m)
above the ground [
56]. The 0.5-inch- (1.2-cm) thick bark becomes scaly
on older stems [
11,
16]. The root system of eastern redbud is long and
coarse with a relatively small number of fine feeder roots near the
surface [
29]. The fruit is a flat, thin-walled legume (pod) 1.5 to 3.9
inches (4-10 cm) long and 0.32 to 0.72 inches (8-18 mm) broad, with
several hard, shiny seeds [
11].
The national champion (1976) eastern redbud from Springfield, Missouri,
measured 47 feet tall (14.3 m), 8.17 inches (20.75 cm) in circumference,
and had a crown spread 36 feet (10.9 m) in diameter [
23].
Unlike most other members of the Fabaceae, eastern redbud does not form
root nodules and does not appear to fix nitrogen [
37].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Distribution
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the term:
naturalThe range of eastern redbud extends from New Jersey and Pennsylvania
west to southern Michigan and southeastern Nebraska; south to eastern
Texas; and east to central Florida [
34]. Its natural range appears to
exclude the Gulf and Atlantic Coastal Plains [
16]. It is extinct from
one locality in extreme southern Ontario [
34].
Texas redbud occurs from southern Oklahoma south to eastern, southern,
and Trans-Pecos Texas; extreme southeastern New Mexico; and northern
Mexico. In Mexico, its range extends from eastern Chihuahua and Coahila
east to Tamps and south to San Luis Potosi and Hidalgo [
34].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Fire Ecology
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
fire regime,
fire tolerant,
forest,
succession,
top-killEastern redbud is rated as fire tolerant due to its habit of sprouting
vigorously after top-kill by fire [
5]. However, it is not reported as a
postfire colonizer, and it is not a member of communities which
experience frequent fire.
At the prairie-forest ecotone, prairie fires limit the spread of woody
vegetation. The lack of fire, perhaps coupled with climatic factors,
has led to the encroachment of woodlands (in which eastern redbud
occurs) onto former prairies [
1,
9]. In eastern Kansas, eastern redbud
occurs in bur oak (Quercus macrocarpa)-chinkapin oak (Q. muehlenbergii)
stands which have established on former tallgrass prairie
(Andropogon-Panicum-Sorghastrum). These forests are normally confined
to galleries along rivers. Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis) and eastern
redbud establish about 10 to 30 years after the cessation of fire (and
following oak establishment) in this area. Long fire-free periods allow
succession to proceed from shade intolerant oaks to more shade tolerant
hickories and eastern redbud. Eastern redbud may replace chinkapin oak
on steep, dry sites. Hackberry is more likely to become dominant on
moist sites [
1]. In southern Illinois, a prairie barren was treated
with four prescribed fires between 1969 and 1973 and subsequently
experienced no fires. Eastern redbud seedlings and saplings were first
recorded on the plots in 1983, 10 years after the last fire [
3].
In central Oklahoma, eastern redbud occurred in post oak (Quercus
stellata)-blackjack oak (Q. marilandica) forest which had not
experienced recent fire, and was not reported for post oak-blackjack oak
savanna which is maintained by fire and edaphic conditions [
30].
FIRE REGIMES : Find fire regime information for the plant communities in which this
species may occur by entering the species name in the
FEIS home page under
"Find FIRE REGIMES".
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Fire Management Considerations
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
climax,
cover,
prescribed fireIn Texas, chaining and burning live oak (Quercus virginiana), white oak
(Q. alba), Texas oak (Q. texana), and Ashe juniper (Juniperus ashei)
resulted in an increase in fire climax species, including Texas redbud.
Fires maintain root sprouters like Texas redbud in a low growing
condition. Prescribed fire is recommended for these areas to cover
approximately 10 to 15 percent of the total area each year (resulting in
a 5- to 10-year rotation) [
21].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Growth Form (according to Raunkiær Life-form classification)
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. More info for the term:
phanerophytePhanerophyte
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Habitat characteristics
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
grassland,
naturalEastern redbud grows on almost any site that is not excessively wet,
excessively dry, or strongly acidic [
11,
14,
18]. Within its natural
range, eastern redbud exhibits a strong preference for, and can be used
as an indicator of, alkaline soils. Eastern redbud occurs in eastern
redcedar communities on calcareous soils [
12]. In Virginia, eastern
redbud tends to occur on alkaline soils high in calcium and magnesium
[
20]. Collier and Longenecker [
15] recommend a soil pH range of 6.0 to
8.0. Best growth of eastern redbud occurs on rich, moist soils, usually
in partial shade [
11]. It is usually not considered drought tolerant
[
18]; however, its ability to tolerate dry conditions is decreased in
full full sun [
14]. Probst [
42] reported that eastern redbud is less
common in oak forests on poor sites than in oak forests on good sites
(defined by oak site indices). The upper elevational limit of eastern
redbud is about 2,200 feet (670 m) in the southeastern portion of its
range [
18]. In Trans-Pecos Texas, eastern redbud ranges from 2,300 to
5,000 feet (701-1524 m) in elevation [
41].
In Trans-Pecos Texas, Mexican redbud occurs in brushy arroyos, canyons,
and limestone hillsides [
41]. In the Konza Prairie of Kansas, eastern
redbud occurs on rocky breaks in the grassland [
45].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Habitat: Cover Types
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. This species is known to occur in association with the following cover types (as classified by the Society of American Foresters):
25 Sugar maple - beech - yellow birch
26 Sugar maple - basswood
27 Sugar maple
40 Post oak - blackjack oak
42 Bur oak
44 Chestnut oak
46 Eastern redcedar
52 White oak - black oak - northern red oak
53 White oak
55 Northern red oak
59 Yellow-poplar - white oak - northern red oak
60 Beech - sugar maple
64 Sassafras - persimmon
65 Pin oak - sweetgum
78 Virginia pine - oak
79 Virginia pine
80 Loblolly pine - shortleaf pine
81 Loblolly pine
87 Sweetgum - yellow-poplar
89 Live oak
110 Black oak
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Habitat: Ecosystem
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. This species is known to occur in the following ecosystem types (as named by the U.S. Forest Service in their Forest and Range Ecosystem [FRES] Type classification):
FRES13 Loblolly - shortleaf pine
FRES14 Oak - pine
FRES15 Oak - hickory
FRES16 Oak - gum - cypress
FRES17 Elm - ash - cottonwood
FRES18 Maple - beech - birch
FRES19 Aspen - birch
FRES32 Texas savanna
FRES33 Southwestern shrubsteppe
FRES38 Plains grasslands
FRES39 Prairie
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Habitat: Plant Associations
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. This species is known to occur in association with the following plant community types (as classified by Küchler 1964):
More info for the term:
forestK082 Mosaic of K074 and K100
K084 Cross Timbers
K089 Black Belt
K099 Maple - basswood forest
K100 Oak - hickory forest
K101 Elm - ash forest
K102 Beech - maple forest
K103 Mixed mesophytic forest
K104 Appalachian oak forest
K106 Northern hardwoods
K110 Northeastern oak - pine forest
K111 Oak - hickory - pine forest
K112 Southern mixed forest
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Immediate Effect of Fire
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
Eastern redbud is easily top-killed by fire but regenerates after fire
by sprouting. Eastern redbud developed clusters of root sprouts after
being top-killed by a prescribed spring fire to discourage the
encroachment of woody species onto a south-central Ohio prairie [
4].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Importance to Livestock and Wildlife
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the term:
treeEastern redbud seeds or pods are eaten by quail, pheasants [
11], other
birds including goldfinch [
27], and deer [
11]. Birds will open pods on
the tree to get at the seeds [
16]. Deer and cattle browse young trees [
53].
Eastern redbud occurs in Ashe juniper (Juniperus ashei) habitat which is
critical to endangered golden-cheeked warblers. The relationship of
eastern redbud to golden-cheeked warblers was not reported (the warblers
are primarily insectivorous) [
32].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Key Plant Community Associations
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the term:
treeEastern redbud occurs in the open or as an understory tree common along
the edge of woods in a variety of habitats [
11,
53]. In Kentucky, it
occurs on exposed limestone cliffs in eastern redcedar (Juniperus
virginiana) communities [
12].
It very commonly occurs with flowering dogwood (Cornus florida) [
54].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Life Form
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
shrub,
treeTree, Shrub
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Management considerations
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
cover,
seedOn southern red oak (Quercus falcata) sites that were clearcut, eastern
redbud increased on plots where flowering dogwood, red maple (Acer
rubrum), and hickory (Carya spp.) were injected with herbicides. This
increase may be in part due to bird dispersed seed since bird activity
was high in this area [
26].
The response of eastern redbud to tebuthiruon or triclopyr treatments
was reported by Stritzke and others [
52]. Neither of the herbicides
used resulted in more than 66 percent kill of eastern redbud, and by 2
years after the treatment, canopy cover of all species had increased to
94 percent (plots with no herbicides averaged 175% canopy cover) [
52].
Picloram has been reported as effectively suppressing sprouting in
redbud [
58].
Eastern redbud is relatively free of serious insect pests and diseases
[
15]. It is fed upon by gypsy moth larvae (later stages) only when
preferred species are not available [
24].
Eastern redbud is rated as moderately sensitive to ozone damage [
25].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Nutritional Value
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
Crude protein, digestibility, and water content were reported for
eastern redbud on untreated plots and plots treated with herbicide and
fire over the course of a growing season [
8].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Occurrence in North America
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
AL AR DE FL GA IL IN KS KY LA
MI MS MO NE NC NJ OH OK PA SC
TN TX VA WV MEXICO
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Other uses and values
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the term:
treeEastern redbud is a popular ornamental [
11]. It is listed among trees
useful for xeriscaping (landscaping for minimal water use) [
40]. It is
sometimes a valuable source of nectar for honey production [
47]. The
flowers may be pickled for use in salads or fried (a common practice in
Mexico). An astringent fluid extract from redbud bark has been used in
treating dysentery [
41].
Eastern redbud is the state tree of Oklahoma [
13].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Palatability
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
Armstrong [
5] lists redbud as moderately preferred browse for
white-tailed deer on the Edwards Plateau, Texas.
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Phenology
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. More info for the term:
treeEastern redbud flowers appear before the leaves from as early as
February in the southeastern United States to May [
11,
16,
56]. In the
southern part of its range, eastern redbud pods are fully grown by the
end of May and ripen by September or October [
16,
56]. The pods split
open in late autumn to winter, sometimes persisting on the tree through
the winter [
18,
56].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Plant Response to Fire
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
density,
frequency,
prescribed fire,
relative dominance,
surface fire,
wildfireIn North Carolina, a 1931 wildfire burned with varying intensity in a
35-year-old oldfield loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) stand. Flowering
dogwood and estern redbud were the most abundant woody species in the
understory and in the shrub/seedling strata of the unburned area 9 years
after the fire. Eastern redbud was recorded for the area that
experienced crown fires but was present at a lower density and frequency
than in the unburned stand. No eastern redbud was recorded for the area
that had experienced surface fire. No specific data on composition of
the plots prior to the fire was reported [
39].
In Alabama, the relative dominance of eastern redbud decreased on plots
that were burned in spring and in fall, as measured from 1 to 3 years
after clearcutting and prescribed fire. By 3 years after a
low-intensity spotty spring fire, however, average height of eastern
redbud was 17 feet (5 m) (as compared to 21 feet (6) on unburned plots).
On plots that had experienced a more uniform, intense fire, average
height of eastern redbud was 8 feet (2.4 m) only 1 year after the fire [
28,
36].
Germinable eastern redbud seeds were present in the seedbank but not
represented in the vegetation of a tallgrass prairie site that was
prescribed burned annually between 1978 and 1984. The seeds were not
reported from unburned sites or from sites that experienced fire at
4-year intervals [
2].
Average crude protein for eastern redbud was slightly higher on plots
that had been treated with herbicide and fire than on untreated plots [
8].
The Research Paper by
Bowles and others 2007 provides information on
postfire responses of several plant species, including eastern redbud,
that was not available when this species review was written.
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Post-fire Regeneration
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
Tree with adventitious-bud root crown/soboliferous species root sucker
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Regeneration Processes
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the terms:
root crown,
scarification,
seed,
softwood,
stratificationEastern redbud reproduces by bird dispersed seeds [
47]. On average,
first reproduction occurs when an individual is about 15 feet tall (4.5
m), although sometimes blooming begins when trees are 5 to 7 feet
(1.5-2.1 m) in height [
14]. Pods may be borne by 5-year-old eastern
redbud, with a maximum reproductive age of 75 years. Good seed crops
usually occur in alternate years [
56]. The seeds exhibit combined
dormancy: internal dormancy plus a hard, impermeable seedcoat [
46]. In
nursery practice, both scarification and cold, moist stratification are
required for germination [
59].
Eastern redbud sprouts from the roots or root crown following topkill [
5].
Eastern redbud can be propagated by softwood cuttings [
17].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Regional Distribution in the Western United States
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. This species can be found in the following regions of the western United States (according to the Bureau of Land Management classification of Physiographic Regions of the western United States):
13 Rocky Mountain Piedmont
14 Great Plains
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Successional Status
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info on this topic. More info for the terms:
climax,
forest,
fruit,
hardwood,
mesic,
relative dominance,
successionFacultative Seral Species
Eastern redbud is moderately tolerant of shade and grows well in full
sun. Flower and fruit production is best in full sun, but eastern
redbud's tolerance of full sunlight decreases in hot and dry areas
[
50,
54]. It has been hypothesized that eastern redbud and similar
midstory trees such as flowering dogwood attain a midstory canopy height
that maximizes interception of sunflecks (transitory periods of full sun
created by gaps in the canopy and the angle of the sun). If this is the
case, eastern redbud requires at least short periods of sunlight for
growth [
54].
Eastern redbud apparently establishes in middle seres, forming a
midstory layer, often with flowering dogwood. In North Carolina,
eastern redbud and flowering dogwood developed as a distinct midstory
under an oldfield shortleaf pine (Pinus echinata) canopy as the stand
approached middle age (85 years) [
7]. In western Tennessee, eastern
redbud was recorded on 28-year-old abandoned agricultural fields, but
not recorded on 3- and 12-year-old sites [
48]. In Texas, primary
succession in gravel pit excavations did not include eastern redbud even
on the 47-year-old site, although eastern redbud was present in adjacent
undisturbed forest [
60]. Eastern redbud is a characteristic midstory
species in mesic southern mixed hardwood forests which succeed
pine-hardwood mixtures, and could therefore be classed as a
late-successional species [
43]. It occurs, for example, in an
old-growth oak forest in northwestern Ohio [
61] and it is present as
seedlings, saplings and mature trees in southern mixed hardwood forest
in north-central Florida [
38]. It may not, however, be stable in some
climax communities: eastern redbud was reported as decreasing in
importance and relative dominance in an oldgrowth oak (Quercus
spp.)-hickory (Carya spp.) forest in Illinois [
49].
Although eastern redbud is not usually described as a pioneer species it
often increases in dominance on sites experiencing disturbance. It is
common on cutover or windthrown areas on calcareous soils [
35]. In
Indiana, a tornado caused severe windthrow in a sugar maple (Acer
saccharum)-Ohio buckeye (Aesculus glabra) stand. Prior to the tornado,
eastern redbud was a minor component in the stand. The most severely
damaged portion of the forest was still mostly open 7 years after the
disturbance and was dominated by sugar maple, elms (Ulmus spp.), Ohio
buckeye, and eastern redbud. Eastern redbud, which increased
dramatically in the first years after the tornado, will probably decline
in importance as taller species begin to close the canopy [
35].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Synonyms
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Taxonomy
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the term:
xericThe currently accepted scientific name for eastern redbud is Cercis
canadensis L. (Fabaceae) [
11]. Texas redbud (C. c. var. texensis [Wats]
Hopkins) is recognized by some authorities [
34]. Others include Mexican
redbud (C. c. var. mexicana [Rose] Hopkins) [
41]. Clark and Bachtell
[
14] report, however, that a common opinion among nursery workers is
that the two varieties represent environmentally induced morphologies
(i.e. more leathery leaves in more xeric conditions) and that C. c. var.
texensis and C. c. var. mexicana are all C. c. var. canadensis.
Information is reported by variety in this write-up.
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Value for rehabilitation of disturbed sites
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
More info for the term:
densityEastern redbud was planted on surface mined sites in Indiana between
1928 and 1975 [
10]. It is apparently no longer used much for this
purpose.
Eastern redbud was present as a volunteer at a density of 40 stems per
acre on a 30-year-old plantation on a surface mined site in Missouri [
57].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Wood Products Value
(
англиски
)
добавил Fire Effects Information System Plants
The wood of eastern redbud is heavy, hard, and close-grained [
11,
16],
but weak [
56]. It is of no commercial value since the trees are rarely
large enough to provide merchantable timber [
11].
- библиографски навод
- Sullivan, Janet. 1994. Cercis canadensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/
Comprehensive Description
(
англиски
)
добавил North American Flora
Cercis canadensis L. Sp. PI. 374. 1753
Cercis canadensis piibcsccns Pursh, Fl. Am. Si-pt. .'^08. 1814. Cercis dilatata Greene. Report. Sp. Nov. 11 : 1 10. 1912. Cercis ellipsoidea Greene, Repert. Sp. Nov. 11: 1 10. 1912. Cercis georgiana Greene, Repert. Sp. Nov. 11: 110. 1912.
Usually a small tree, but sometimes 16 m. high, the twigs glabrous. Leaves cordate or truncate at base, 5-15 cm. broad, short-pointed or obtuse, usually glabrous but sometimes sparingly pubescent beneath; flowers several, in sessile umbels or fascicles; pedicels 8-25 mm. long, slender; corolla pink-purple, about S mm. long; legume glabrous, 5-7.5 cm. long, 12 mm. wide.
Type locality: Virginia.
Distribution: Ontario to Florida, Michigan, Nebraska. Oklahoma and Texas.
- библиографски навод
- Nathaniel Lord Britton and Joseph Nelson Rose. 1928. (ROSALES); MIMOSACEAE. North American flora. vol 23(1). New York Botanical Garden, New York, NY
Associated Forest Cover
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Redbud is a regular but usually not a common understory component
of many forest types throughout the Eastern United States. It is
not a commercial timber species, and although it grows in many
forest cover types, it is not listed in all of them by the
Society of American Foresters (4).
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Climate
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
A wide range of climatic conditions are present in the large
geographical range of redbud. Mean annual precipitation is less
than 510 mm (20 in) in dry south Texas and approximately 1270 mm
(50 in) in moist central Florida. Mean annual snowfall in the
northern perimeter of redbud is about 90 cm (35 in). Mean January
temperatures vary from -8° C (18° F) to 16° C (61°
F) within the native range of redbud. Mean July temperatures vary
from about 21° C (70° F) in southern Pennsylvania to 26°
C (79° F) in central Florida. Frost-free days can vary from
160 to 300 days.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Damaging Agents
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Redbud is a host to a variety of insects,
but damage is not normally severe. Bark and phloem borers include
three species of Hypothenemus, and Pityophthorus
lautus (2). A seed beetle, Gibbobruchus mimus, breeds
in the seed of redbud.
Numerous wood borers have been found in redbud. Agrilus
otiosus, three species of Hypothenemus, three species
of Micracis, two species of Microcisella,
Pityophthorus lautus, Ptosima gibbicollis, and Thysanoes
fimbricornis all inhabit portions of the wood of redbud.
Other insects feed on the leaves of redbud. The redbud leaffolder,
Fascista cercerisella, feeds on leaves which the larvae
web together. The grape leaffolder, Desmia funeralis, an
important pest of grape, also feeds on redbud. The Japanese
weevil, Callirhopalus bifasciatus, and Norape ovina
both consume redbud leaves.
Other insects feed on redbud by extracting juices from the plant.
The twolined spittlebug, Prosapia bicincta, has been
recorded feeding on redbud. The terrapin scale, Mesolecanium
nigrofasciatum, and San Jose scale, Quadraspidiotus
perniciosus, like most of the other redbud parasites, inhabit
a variety of hosts including redbud. The periodical cicada, Magicicada
septendecim, lays its eggs in more than 70 species of trees
and other plants, including redbud.
There are three main diseases of redbud: leaf anthracnose, Mycosphaerella
cercidicola, Botryosphaeria canker, and Verticillium wilt
(6). The most serious is the canker Botryosphaeria ribis or
its variety chromogena. The species is mainly a saprobe;
the variety is a parasite. This variety produces stem and twig
lesions and entire groves of redbuds have been killed by this
disease. Verticillium wilt (Verticillium albo-atrum) sometimes
kills redbuds, especially in the Midwestern United States. Redbud
is vulnerable to Texas root rot (Phymatotrichum omnivorum),
but redbud is not commonly grown in its range. A variety of
sap and heart rots also infect eastern redbud.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Flowering and Fruiting
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Redbud flowers are pink to reddish
purple, and rarely white. They are home on pedicels in clusters
of two to eight. Flowers are produced from small buds on old
twigs, branches, and trunks. Flowers are bisexual and the tree is
self-pollinating. Flowering usually occurs sometime from March to
May and precedes leafing. In Indiana, the tree requires 30 days
of temperatures averaging more than 10° C (50° F) .
Previous winter chilling also enhances flowering (11).
Pollination is usually accomplished by bees. After 2 or 3 weeks
leaves appear and the flowers drop. The ovaries of one to several
flowers in most flower clusters enlarge and develop into fruits
that reach their full size by midsummer (13). Fruits are flat
reddish-brown pods about 1.3 cm (0.5 in) wide and 5 to 10 cm (2
to 4 in) long (16). Each fruit contains 4 to 10 brown, hard,
compressed bean-like seeds, each about 6mm (0.25 in) long. The
fruits remain on the tree until after leaf fall; some persist
throughout winter (15).
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Genetics
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Donselman (3) investigated morphological variation in
trees grown from seed collected from 13 diverse locations in the
range of redbud. He concluded that trees from more xeric
locations in the Southwestern and western portions of the range
exhibited adaptations to high solar radiation, drying winds, low
humidity, low soil moisture, and other environmental factors
associated with high evapotranspiration. Leaves from those plants
were thicker and smaller, had increased pubescence, and showed
more efficient stomatal geometry than trees from mesic locations.
Two subspecies of redbud have been identified: Texas redbud (Cercis
canadensis var. texensis) found in southern Oklahoma,
Trans-Pecos Texas, and southeastern New Mexico; and eastern
redbud (C. canadensis var. canadensis) found in
the remainder of the range of redbud (9). Another native Cercis
species, California redbud (C. occidentalis), is
found in Utah, Nevada, California and Arizona.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Growth and Yield
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Development of young redbud to the
flowering stage is rapid. Young redbuds have been observed first
flowering when less than 7 years old but do not fruit the first
year of blossoming. Annual cambial growth begins just before
flowering and shoot growth usually begins during flowering (11).
In Indiana terminal growth of saplings started when the weekly
mean of the daily mean temperature reached 13° C (55°
F). Maximum growth was reached the fourth week and growth ceased
after 6 to 10 weeks under low soil moisture conditions. With
adequate soil moisture, terminal growth continued until frost.
More than 1076 lux (100 lumens/ft²) of light and more than
13 hours of daylight daily are needed to maintain terminal growth
of saplings.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Reaction to Competition
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
As redbuds grow and mature they
become less shade tolerant. Old trees usually suffer from heart
rot and cannot normally tolerate severe competition and shade.
Redbud is most accurately classed as tolerant of shade.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Rooting Habit
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Redbud develops a deep taproot that
descends rapidly the first few years if the soil permits. Initial
growth depends on soil moisture and the absence of a tight clay
subsoil. If impenetrable subsoils are present the taproot grows
horizontally. Secondary roots appear when the taproot is 5 to 8
cm (2 to 3 in) long and grow rapidly.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Seed Production and Dissemination
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Seeds are released by
the opening of fruit sutures or decay of the fruit wall. Most
seeds are dispersed during fall and winter by wind and animals.
Many seeds are injured by insects. Those that fall to the ground
usually remain dormant for several years (1).
For artificial propagation, seeds should be collected, cleaned,
and dried when ripe to avoid insect damage. Dried seeds can be
stored in sealed glass or metal containers at 2' to 5' C (35' to
41° F). Seed treatment is necessary for propagation because
redbud shows delayed germination due to impermeability of the
seed coat to water and dormancy of the embryo (1). The seed coat
can be made permeable to water by mechanical scarification or by
immersion in boiling water or in concentrated sulfuric acid for
about 30 minutes. After scarifying, seeds should be stratified in
moist sand at about 5° C (41' F) for 5 to 8 weeks (14).
Prepared seeds should be sown in well-prepared seedbeds in late
April or early May (14). Moist soil should cover seeds at a
maximum depth of 0.5 em (0.2 in). Propagation can also be
accomplished by layering or cuttings.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Seedling Development
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Approximate site characteristics and
seedling vigor determine seedling establishment. Germination is
epigeal (14). Under optimum conditions seedlings can grow 0.3 m
(1 ft) in height the first growing season. Continuous terminal
growth is related to light intensity, photoperiod, and
temperature (11). Once established, seedlings can endure much
shading.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Soils and Topography
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Redbud is found on a variety of sites ranging from xeric to mesic
but grows better on moist, well-drained sites. It is normally
more abundant on south-facing slopes where sunlight is more
intense and there is less plant competition (11). This species
does not usually grow on flooded sites because it cannot endure
inundation or survive in poorly aerated soils.
The tree grows well in a variety of soil textures but is not found
in coarse sands (11). It requires some fine or colloidal
material. Redbud is tolerant of a wide pH range but grows best
where the pH is above 7.5. It is prevalent on limestone outcrops
and on alkaline soils derived from them (11,12). Redbud is
tolerant of nutrient deficiencies. Therefore, less competition
can occur from associated trees that are less vigorous on the
nutrient deficient sites. In Indiana no relationship was noted
between distribution of redbud and soil calcium or magnesium.
Redbud is found on soils of most soil orders, but most commonly
on those of the orders Alfisols and Mollisols.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Special Uses
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
The eastern redbud is extensively planted as an ornamental
throughout the Eastern United States. It is tolerant of a wide
range of site conditions, is not especially vulnerable to insects
or diseases, is relatively easy to maintain, and makes a
beautiful shrub or small tree, especially when flowering.
Bark of redbud has been used as an astringent in the treatment of
dysentery. Flowers of the tree can be put into salads or fried
and eaten (16). There is some documented wildlife use of redbud
fruit. Cardinals have been observed feeding on the seeds, and
seeds have been consumed by ring-necked pheasants rose-breasted
grosbeaks (5), and bobwhites (7) White-tailed deer and gray
squirrels have also been observed feeding on the seeds (5).
Flowers of the tree are regarded as important in the production
of honey by bees (10).
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Vegetative Reproduction
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
No information available.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Distribution
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
The range of eastern redbud is from New Jersey and southern
Pennsylvania northwest to southern Michigan, southwest into
southeastern Nebraska, south to central Texas, and east to
central Florida (8). A disjunct population of redbud extends from
the Trans-Pecos and south Texas into Mexico.
-The native rane of eastern redbub.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Brief Summary
(
англиски
)
добавил Silvics of North America
Leguminosae -- Legume family
James G. Dickson
Eastern redbud (Cercis canadensis) is a small, short-lived
deciduous tree found throughout the eastern United States. Redbud
is also known as Judas-tree. According to legend, Judas Iscariot
hanged himself from a branch of the European species Cercis
siliquastrum (13). Eastern redbud is a strikingly conspicuous
tree in the spring because it flowers before other tree leaves
form. The wood is heavy, hard, and close-grained, but because of
the small size and irregular shape of the tree it is of no
commercial value as a source of lumber. This tree is most valued
as an ornamental and is extensively planted.
- лиценца
- cc-by-nc
- авторски права
- USDA, Forest Service
Physical Description
(
англиски
)
добавил USDA PLANTS text
Perennial, Trees, Woody throughout, Stems erect or ascending, Stems greater than 2 m tall, Stems solid, Stems or young twigs glabrous or sparsely glabrate, Leaves absent at flowering time, Leaves alternate, Leaves petiolate, Stipules deciduous, Stipules free, Leaves simple, or appearing so, Leaf or leaflet margins entire, Leaflets 1, Leaves glabrous or nearly so, Flowers in axillary clusters or few-floweredracemes, 2-6 flowers, Inflorescence umbel-like or subumbellate, Inflorescence cauliferous, Inflorescence axillary, Flowers zygomorphic, Calyx 5-lobed, Calyx glabrous, Petals separate, Corolla papilionaceous, Petals clawed, Petals pinkish to rose, Banner petal ovoid or obovate, Wing petals narrow, oblanceolate to oblong, Wing tips obtuse o r rounded, Keel tips obtuse or rounded, not beaked, Stamens 9-10, Stamens completely free, separate, Filaments hairy, villous, Style terete, Fruit a legume, Fruit stipitate, Fruit unilocular, Fruit freely dehiscent, Fruit tardily or weakly dehiscent, Fruit elongate, straight, Fruits winged, carinate, or samaroid, Fruit or valves persistent on stem, Fruit exserted from calyx, Fruit glabrous or glabrate, Fruit 3-10 seeded, Seeds ovoid to rounded in outline, Seed surface smooth, Seeds olive, brown, or black.
Cercis canadensis
(
астурски
)
добавил wikipedia AST
Cercis canadensis ye una especie arbórea de la familia de les lleguminoses Fabaceae, subfamilia Caesalpinioideae, xéneru Cercis, orixinaria del este de Norteamérica dende Ontario meridional, Canadá, escontra'l sur hasta'l norte de Florida, Estaos Xuníos
Descripción
Trátase d'un parrotal grande o árbol pequeñu, que crez hasta los 6-9 metros con un anchor de 8–10 m. Por regla xeneral, el tueru ye curtiu, de cutiu retorcigañáu tueru y les cañes estiéndense. Un árbol de 10 años d'edá, polo xeneral, va tener alredor de 5 m d'altor. La corteza ye de color escuru, castañal acoloratada, llisa, más tarde escamosa con crestes un tanto evidentes, dacuando con mancha color marrón. Les ramines son delgaes y en zigzag, cuasi de color negru, con llurdios lenticeles más clares; de primeres tienen un color castañu polencu, depués escurécense. La madera ye de color castañu acoloratáu escuru; pesada, dura, non fuerte. Los biltos d'iviernu son bien pequeños, arrondaes y de color coloráu escuru a castañal. Les fueyes son alternes, simples, en forma de corazón o llargamente ovaes, colos cantos enteros , de 7–12 cm de llargu y son amplies, delgaes y como de papel, y pueden tener un viesu llixeramente velloso. Salen de la yema doblaes a lo llargo de la llinia de la nervadura central, verde escuru, cuando tán dafechu desenvueltos convertir en llises, de color verde escuru percima, más pálidu per debaxo. Na seronda tórnense de color mariellu claru y brillosu. Pecíolus delgaos, cilíndricos, ampliaos na base. Estípules caduques.
![src=]()
Flores de
Cercis canadensis.
![src=]()
Fueyes de
Cercis canadensis "Forest Pansy".
Les flores son vistoses, de color magenta rosáu de claru a escuru, de 1,5 cm de llargu, qu'apaecen en recímanos de marzu a mayu, en tarmos desnudos primero que les fueyes. Perfectu color rosa, tien de 4 a 8 xuntes, en fascículos qu'apaecen nes axiles de les fueyes o pola caña, dacuando nel mesmu tueru. El mota ye de color coloráu escuru, acampanáu, oblicuu, con cinco dientes, inxeríos na yema. La corola ye papilonácea, con cinco pétalos, cuasi iguales, de color rosa o de color rosa, el pétalu cimeru más pequeñu, zarráu nel so orixe poles nales, y arrodiáu polos pétalos de quilla más amplios. Tien 10 estames, ensertaos en dos fileres nun discu delgáu, llibre, la fila interior más curtia que les otres. El pistilu ye un ovariu cimeru, ensertáu de forma oblicua na parte inferior del tubu de la mota, estipitado; estilu carnosu, curváu, na punta tien un estigma obtusu. Les flores son polinizaes poles abeyes de llingua llarga como les abeyes d'arándanos y Xylocopa virginica. Les abeyes de llingua curtia, aparentemente, nun puede algamar los nectarios.
El frutu ye como una llenteya, esplanáu, secu, marrón, desigual y oblongo, agudu nos estremos. Estruyíu, con puntes de los restos del estilu, 5–10 cm de llongura que contienen granes planes, elíptiques y de color castañu 6 mm de llargu, que maurecen d'agostu a ochobre. Pueden faese granar per primer inmersión n'agua fervida (99 °C) (bien caliente) mientres un minutu y depués echar nuna olla (ensin ferver les granes); cotiledones ovalaos y planos.[2]
Crez rápido. Na naturaleza, ye un árbol nativu frecuente nel sotobosque, en montes y sebes mistes. Les fueyes son consumíes poles gates de dalgunos lepidópteros, por casu, Automeris io. Munchos árboles son maneros y nun producen nengún frutu.
Distribución
Alcuéntrase nes tierres baxes riques en tol valle del ríu Mississippi, va crecer a la solombra y, de cutiu conviértese nuna trupa maleza nel monte. Bien abondosu en Arkansas, Oklahoma y nel este de Texas. Ye malo d'atopar más al norte.
Ye difícil que creza escontra l'oeste, como en Kansas occidental y Coloráu, pos nun hai abonda agua. El so parte más septentrional de la área de distribución ye'l sur de Nueva Inglaterra. Crez bien nel estáu de Nueva York, en Nueva Jersey y escontra el sur.
Usos
Los nativos americanos consumíen flores crudes o fervíes de Cercis canadensis, según les granes turraes. En delles partes del sur de los Apalaches, les ramines verdes del Cercis canadensis utilícense como condimento pa la caza como'l venáu y la zarigüeya. Por cuenta de esto, nestes zones de monte dacuando conozse al Cercis canadensis como spicewood tree ("árbol de especia"). Los componentes nutricionales nes partes comestibles del C. canadensis son:
Tamién se planta enforma como árbol ornamental paisaxísticu.
El Cercis canadensis ye l'árbol del estáu d'Oklahoma.
Taxonomía
Cercis canadensis describióse por Carlos Linneo y espublizóse en Species Plantarum 1: 374. 1753.[4]
- Etimoloxía
Cercis: nome xenéricu que remanez del griegu antiguu "kerkis", que designaba al Ciclamor.
canadensis: epítetu xeográficu qu'alude al so localización en Canadá.
- Variedaes
-
Cercis canadensis var. mexicana (Britton & Rose) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis canadensis var. orbiculata (Greene) Barneby
-
Cercis canadensis var. texensis (S.Watson) M.Hopkins
- Sinonimia
-
var. mexicana (Britton & Rose) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis mexicana Britton & Rose
-
var. orbiculata (Greene) Barneby
-
Cercis arizonica Rose ex N. N. Dodge
-
Cercis occidentalis var. orbiculata (Greene) Tidestr.
-
Cercis orbiculata Greene
-
var. texensis (S.Watson) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis reniformis A.Gray[5]
Ver tamién
Referencies
Bibliografía
- CONABIO. 2009. Catálogu taxonómicu d'especies de Méxicu. 1. In Capital Nat. Méxicu. CONABIO, Mexico City.
- Correll, D. S. & M. C. Johnston. 1970. Man. Vasc. Pl. Texas i–xv, 1–1881. The University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson.
- Cronquist, A.J., A. H. Holmgren, N. H. Holmgren, Reveal & P. K. Holmgren. 1989. Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West, U.S.A., FABALES. 3B: 1–279. In A.J. Cronquist, A. H. Holmgren, N. H. Holmgren, J. L. Reveal & P. K. Holmgren (eds.) Intermount. Fl.. Hafner Pub. Co., New York.
- Fernald, M. 1950. Manual (ed. 8) i–lxiv, 1–1632. American Book Co., New York.
- Gleason, H. A. 1968. The Choripetalous Dicotyledoneae. vol. 2. 655 pp. In H. A. Gleason Ill. Fl. N. O.S. (ed. 3). New York Botanical Garden, New York.
- Gleason, H. A. & A.J. Cronquist. 1991. Man. Vasc. Pl. N.Y. O.S. (ed. 2) i–910. New York Botanical Garden, Bronx.
- Great Plains Flora Association. 1986. Fl. Great Plains i–vii, 1–1392. University Press of Kansas, Lawrence.
- Isely, D. 1990. Leguminosae (Fabaceae). 3(2): xix, 1–258. In Vasc. Fl. S.Y. O. S.. The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill.
- Radford, A. Y., H. Y. Ahles & C. R. Bell. 1968. Man. Vasc. Fl. Carolinas i–lxi, 1–1183. University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill.
- Schwegman, J. Y. 1991. The Vascular Flora of Langham Island, Kankakee County, Illinois. Erigenia 11: 1–8.
Enllaces esternos
Biltos preparaos p'abrir a mediaos de marzu.
 Esta páxina forma parte del wikiproyeutu Botánica, un esfuerciu collaborativu col fin d'ameyorar y organizar tolos conteníos rellacionaos con esti tema. Visita la páxina d'alderique del proyeutu pa collaborar y facer entrugues o suxerencies.
Esta páxina forma parte del wikiproyeutu Botánica, un esfuerciu collaborativu col fin d'ameyorar y organizar tolos conteníos rellacionaos con esti tema. Visita la páxina d'alderique del proyeutu pa collaborar y facer entrugues o suxerencies.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia authors and editors
Cercis canadensis: Brief Summary
(
астурски
)
добавил wikipedia AST
Cercis canadensis Cercis canadensis ye una especie arbórea de la familia de les lleguminoses Fabaceae, subfamilia Caesalpinioideae, xéneru Cercis, orixinaria del este de Norteamérica dende Ontario meridional, Canadá, escontra'l sur hasta'l norte de Florida, Estaos Xuníos
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia authors and editors
Arbre de l'amor americà
(
каталонски; валенсиски
)
добавил wikipedia CA
L'arbre de l'amor americà[1] (Cercis canadensis) és una de les espècies del gènere Cercis, que als Estats Units s'anomenen Redbuds.
És un arbust gros o un arbre petit de la família Fabaceae, natiu de l'est de Nord-amèrica des del sud d'Ontàrio, al Canadà, fins al nord de Florida, Estats Units.
Sol créixer fins als 8-12 m d'altura.
Les flors destaquen, van des del rosa clar al rosa fosc, fan 1.5 cm de llarg, apareixen en grups de març a maig, a llocs nuus abans de les fulles.
En jardineria, s'usa aquesta espècie com a planta ornamental.
Les espècies de Cercis Cercis mexicana, Cercis reniformis i Cercis texensis són considerades per algunes fonts subespècies del Cercis canadensis.
Imatges
Brot de Cercis canadensis preparat per obrir-se a mitjans de maig.
Referències
Enllaços externs
En altres projectes de
Wikimedia:
Commons (Galeria) Commons (Categoria)  Viquiespècies
Viquiespècies
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autors i editors de Wikipedia
Arbre de l'amor americà: Brief Summary
(
каталонски; валенсиски
)
добавил wikipedia CA
L'arbre de l'amor americà (Cercis canadensis) és una de les espècies del gènere Cercis, que als Estats Units s'anomenen Redbuds.
És un arbust gros o un arbre petit de la família Fabaceae, natiu de l'est de Nord-amèrica des del sud d'Ontàrio, al Canadà, fins al nord de Florida, Estats Units.
Sol créixer fins als 8-12 m d'altura.
Les flors destaquen, van des del rosa clar al rosa fosc, fan 1.5 cm de llarg, apareixen en grups de març a maig, a llocs nuus abans de les fulles.
En jardineria, s'usa aquesta espècie com a planta ornamental.
Les espècies de Cercis Cercis mexicana, Cercis reniformis i Cercis texensis són considerades per algunes fonts subespècies del Cercis canadensis.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autors i editors de Wikipedia
Cercis canadensis
(
англиски
)
добавил wikipedia EN
Cercis canadensis, the eastern redbud, is a large deciduous shrub or small tree, native to eastern North America from southern Michigan south to central Mexico, west to New Mexico. Species thrive as far west as California and as far north as southern Ontario, roughly corresponding to USDA hardiness zone 5b.[2] It is the state tree of Oklahoma.
Description
The eastern redbud typically grows to 6–9 m (20–30 ft) tall with an 8–10 m (26–33 ft) spread. It generally has a short, often twisted trunk and spreading branches. A 10-year-old tree will generally be around 5 m (16 ft) tall. The bark is dark in color, smooth, later scaly with ridges somewhat apparent, sometimes with maroon patches. The twigs are slender and zigzag, nearly black in color, spotted with lighter lenticels. The winter buds are tiny, rounded and dark red to chestnut in color. The leaves are alternate, simple, and heart shaped with an entire margin, 7–12 cm (3–4.5 in) long and wide, thin and papery, and may be slightly hairy below.
The flowers are showy, light to dark magenta pink in color, 1.5 cm (1⁄2 in) long, appearing in clusters from spring to early summer, on bare stems before the leaves, sometimes on the trunk itself. There are cultivars with white flowers. The flowers are pollinated by long-tongued bees such as blueberry bees and carpenter bees. Short-tongued bees cannot reach the nectaries. The fruit are flattened, dry, brown, pea-like pods, 5–10 cm (2–4 in) long that contain flat, elliptical, brown seeds 6 mm (1⁄4 in) long, maturing in August to October.

Cercis canadensis 'Forest Pansy' leaves in July.
- Bark: Red brown, with deep fissures and scaly surface. Branchlets at first lustrous brown, later become darker.
- Wood: Dark reddish brown; heavy, hard, coarse-grained, not strong. Sp. gr., 0.6363; weight of cu. ft. 39.65 lbs.
- Winter buds: Chestnut brown, obtuse, one-eighth inch long.
- Cotyledons oval, flat
- Leaves: Alternate, simple, heart-shaped or broadly ovate, two to five inches long, five to seven-nerved, cordate or truncate at the base, entire, acute. They come out of the bud folded along the line of the midrib, tawny green; when they are full grown they become smooth, dark green above, paler beneath. In autumn they turn bright clear yellow. Petioles slender, terete, enlarged at the base. Stipules caducous.
- Flowers: April, May, before and with the leaves, papilionaceous. Perfect, rose color, borne four to eight together, in fascicles which appear at the axils of the leaves or along the branch and sometimes on the trunk itself.
- Calyx: Dark red, campanulate, oblique, five-toothed, imbricate in bud.
- Corolla: Papilionaceous, petals five, nearly equal, pink or rose color, upper petal the smallest, enclosed in the bud by the wings, and encircled by the broader keel petals.
- Stamens: Ten, inserted in two rows on a thin disk, free, the inner row rather shorter than the others.
- Pistil: Ovary superior, inserted obliquely in the bottom of the calyx tube, stipitate; style fleshy, incurved, tipped with an obtuse stigma.
- Fruit: Legume, slightly stipitate, unequally oblong, acute at each end. Compressed, tipped with the remnants of the style, straight on upper and curved on the lower edge. Two and a half to three inches long, rose color, full grown by midsummer, falls in early winter. Seeds ten to twelve, chestnut brown, one-fourth of an inch long.
Ecological benefits
The leaves are eaten by the caterpillars of some Lepidoptera—for example, Henry's elfin, the redbud leaffolder, the red-humped caterpillar (which can cause extensive defoliation in late summer but generally does no lasting harm to a healthy tree),[3] the fall webworm (also a late-season defoliator),[2] the white flannel moth, the American dagger moth, the grape leaffolder, and the Io moth.
Cultivation
Cercis canadensis is grown in parks and gardens, with several cultivars being available. The cultivars 'Forest Pansy'[4] and 'Ruby Falls'[5] have gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit (confirmed 2017).[6] Both are cultivated for their showy purple leaves, which turn brilliant shades of red and orange in the fall (autumn). 'Ruby Falls' is a weeping form.
In the wild, eastern redbud is a frequent native understory tree in mixed forests and hedgerows. It is also much planted as a landscape ornamental plant.
In the United States, this tree is difficult to grow farther west into arid areas west of western Kansas and Colorado, as there is not enough rain. There has been success growing the tree in Columbus, Wisconsin, whose cultivar has become known as the "Columbus strain" and is a seed source for nurseries. Seeds can be made to germinate by first dipping in boiled (99 °C) water for one minute and then sowing in a pot (do not boil the seeds).[7]
Uses
The flowers can be eaten fresh or fried.[8]
In some parts of southern Appalachia, green twigs from the eastern redbud are used as seasoning for wild game such as venison and opossum. Because of this, in these mountain areas the eastern redbud is sometimes known as the spicewood tree.
Native Americans consumed redbud flowers raw or boiled, and ate roasted seeds. Analysis of nutritional components in edible parts of eastern redbud reported that the flower extract contains anthocyanins, green developing seeds contained proanthocyanidin, and linolenic, α-linolenic, oleic and palmitic acids are present in seeds.[9]
References
-
^ IUCN SSC Global Tree Specialist Group.; Botanic Gardens Conservation International; et al. (BGCI) (2020). "Cercis canadensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T33892A155693644. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-1.RLTS.T33892A155693644.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
-
^ a b Gilman, Edward F.; Watson, Dennis G. (November 1993). "Cercis canadensis 'Flame': 'Flame' Eastern Redbud" (PDF). Environmental Horticulture Department, Florida Cooperative Extension Service, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
-
^ "Problems With Forest Pansies". Home Guides | SF Gate. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
-
^ "RHS Plant Selector Cercis canadensis 'Forest Pansy'". Apps.rhs.org.uk. Retrieved 2013-06-13.
-
^ "RHS Plantfinder - Cercis canadensis 'Ruby Falls'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 21 January 2018.
-
^ "AGM Plants - Ornamental" (PDF). Royal Horticultural Society. July 2017. p. 16. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
-
^ Keeler, Harriet L. (1900). Our Native Trees and How to Identify Them. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 104–108.
-
^ Little, Elbert L. (1994) [1980]. The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Trees: Western Region (Chanticleer Press ed.). Knopf. p. 491. ISBN 0394507614.
-
^ Laura J. Hunter, et al. 2006. Analysis of nutritional components in edible parts of eastern redbud (Cercis canadensis L.). 62nd Southwest Regional American Chemical Society Meeting, Houston, Texas.

- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia authors and editors
Cercis canadensis: Brief Summary
(
англиски
)
добавил wikipedia EN
Cercis canadensis, the eastern redbud, is a large deciduous shrub or small tree, native to eastern North America from southern Michigan south to central Mexico, west to New Mexico. Species thrive as far west as California and as far north as southern Ontario, roughly corresponding to USDA hardiness zone 5b. It is the state tree of Oklahoma.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia authors and editors
Cercis canadensis
(
шпански; кастиљски
)
добавил wikipedia ES
El amor del Canadá o ciclamor del Canadá[2] (Cercis canadensis) es una especie arbórea de la familia de las leguminosas Fabaceae, subfamilia Caesalpinioideae, género Cercis, originaria del este de Norteamérica desde Ontario meridional, Canadá, hacia el sur hasta el norte de Florida, Estados Unidos y el este de México.[3]
Descripción
Se trata de un arbusto grande o árbol pequeño, que crece hasta los 6-9 metros con una anchura de 8–10 m. Por regla general, el tronco es corto, a menudo retorcido tronco y las ramas se extienden. Un árbol de 10 años de edad, en general, tendrá alrededor de 5 m de altura. La corteza es de color oscuro, castaño rojizo, lisa, más tarde escamosa con crestas un tanto evidentes, a veces con manchas color marrón. Las ramitas son delgadas y en zigzag, casi de color negro, con manchas lenticelas más claras; al principio tienen un color castaño lustroso, luego se oscurecen. La madera es de color castaño rojizo oscuro; pesada, dura, no fuerte. Los brotes de invierno son muy pequeños, redondeadas y de color rojo oscuro a castaño. Las hojas son alternas, simples, en forma de corazón o ampliamente ovadas, con los bordes enteros, de 7–12 cm de largo y son amplias, delgadas y como de papel, y pueden tener un envés ligeramente velloso. Salen de la yema dobladas a lo largo de la línea de la nervadura central, verde oscuro, cuando están completamente desarrollados se convierten en lisas, de color verde oscuro por encima, más pálido por debajo. En otoño se tornan de color amarillo claro y brillante. Pecíolos delgados, cilíndricos, ampliados en la base. Estípulas caducas.
![src=]()
Flores de
Cercis canadensis.
![src=]()
Hojas de
Cercis canadensis "Forest Pansy".
Las flores son vistosas, de color magenta rosado de claro a oscuro, de 1,5 cm de largo, que aparecen en racimos de marzo a mayo, en tallos desnudos antes que las hojas. Perfecto color rosa, tiene de 4 a 8 juntas, en fascículos que aparecen en las axilas de las hojas o por la rama, a veces en el mismo tronco. El cáliz es de color rojo oscuro, acampanado, oblicuo, con cinco dientes, imbricados en la yema. La corola es papilonácea, con cinco pétalos, casi iguales, de color rosa o de color rosa, el pétalo superior más pequeño, encerrado en su origen por las alas, y rodeado por los pétalos de quilla más amplios. Tiene 10 estambres, insertados en dos filas en un disco delgado, libre, la fila interior más corta que las otras. El pistilo es un ovario superior, insertado de forma oblicua en la parte inferior del tubo del cáliz, estipitado; estilo carnoso, curvado, en la punta tiene un estigma obtuso. Las flores son polinizadas por las abejas de lengua larga como las abejas de arándanos y Xylocopa virginica. Las abejas de lengua corta, aparentemente, no puede alcanzar los nectarios.
El fruto es como una lenteja, aplanado, seco, marrón, desigual y oblongo, agudo en los extremos. Comprimido, con puntas de los restos del estilo, 5–10 cm de largo que contienen semillas planas, elípticas y de color castaño 6 mm de largo, que maduran de agosto a octubre. Se pueden hacer germinar por primera inmersión en agua hervida (99 °C) (muy caliente) durante un minuto y luego echar en una olla (sin hervir las semillas); cotiledones ovalados y planos.[4]
Crece rápidamente. En la naturaleza, es un árbol nativo frecuente en el sotobosque, en bosques y setos mixtos. Las hojas son consumidas por las orugas de algunos lepidópteros, por ejemplo, Automeris io. Muchos árboles son estériles y no producen ningún fruto.
Distribución
Se encuentra en las tierras bajas ricas en todo el valle del río Misisipi, crecerá a la sombra y, a menudo se convierte en una densa maleza en el bosque. Muy abundante en Arkansas, Oklahoma y en el este de Texas. Es difícil de encontrar más al norte.
Es difícil que crezca hacia el oeste, como en Kansas occidental y Colorado, pues no hay suficiente agua. Su parte más septentrional del área de distribución es el sur de Nueva Inglaterra. Crece bien en el estado de Nueva York, en Nueva Jersey y hacia el sur.
En México se distribuye desde Nuevo León hasta Veracruz e Hidalgo.[5][3]
Usos
Los nativos americanos consumían flores crudas o hervidas de Cercis canadensis, así como las semillas tostadas. En algunas partes del sur de los Apalaches, las ramitas verdes del Cercis canadensis se utilizan como condimento para la caza como el ciervo y la zarigüeya. Debido a esto, en estas zonas de montaña a veces se conoce al Cercis canadensis como spicewood tree ("árbol de especia"). Los componentes nutricionales en las partes comestibles del C. canadensis son:
También se planta mucho como árbol ornamental paisajístico.
Cercis canadensis es el árbol del estado de Oklahoma.
Taxonomía
Cercis canadensis fue descrita por Carlos Linneo y publicado en Species Plantarum 1: 374. 1753.[7]
- Etimología
Cercis: nombre genérico que deriva del griego antiguo "kerkis", que designaba al Ciclamor.
canadensis: epíteto geográfico que alude a su localización en Canadá.
- Variedades
-
Cercis canadensis var. mexicana (Britton & Rose) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis canadensis var. orbiculata (Greene) Barneby
-
Cercis canadensis var. texensis (S.Watson) M.Hopkins
- Sinonimia
-
var. mexicana (Britton & Rose) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis mexicana Britton & Rose
-
var. orbiculata (Greene) Barneby
-
Cercis arizonica Rose ex N. N. Dodge
-
Cercis occidentalis var. orbiculata (Greene) Tidestr.
-
Cercis orbiculata Greene
-
var. texensis (S.Watson) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis reniformis A.Gray[8]
Galeria
Brotes por abrirse a mediados de marzo.
Referencias
Bibliografía
- CONABIO. 2009. Catálogo taxonómico de especies de México. 1. In Capital Nat. México. CONABIO, Mexico City.
- Correll, D. S. & M. C. Johnston. 1970. Man. Vasc. Pl. Texas i–xv, 1–1881. The University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson.
- Cronquist, A.J., A. H. Holmgren, N. H. Holmgren, Reveal & P. K. Holmgren. 1989. Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West, U.S.A., FABALES. 3B: 1–279. In A.J. Cronquist, A. H. Holmgren, N. H. Holmgren, J. L. Reveal & P. K. Holmgren (eds.) Intermount. Fl. Hafner Pub. Co., New York.
- Fernald, M. 1950. Manual (ed. 8) i–lxiv, 1–1632. American Book Co., New York.
- Gleason, H. A. 1968. The Choripetalous Dicotyledoneae. vol. 2. 655 pp. In H. A. Gleason Ill. Fl. N. U.S. (ed. 3). New York Botanical Garden, New York.
- Gleason, H. A. & A.J. Cronquist. 1991. Man. Vasc. Pl. N.E. U.S. (ed. 2) i–910. New York Botanical Garden, Bronx.
- Great Plains Flora Association. 1986. Fl. Great Plains i–vii, 1–1392. University Press of Kansas, Lawrence.
- Isely, D. 1990. Leguminosae (Fabaceae). 3(2): xix, 1–258. In Vasc. Fl. S.E. U. S. The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill.
- Radford, A. E., H. E. Ahles & C. R. Bell. 1968. Man. Vasc. Fl. Carolinas i–lxi, 1–1183. University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill.
- Schwegman, J. E. 1991. The Vascular Flora of Langham Island, Kankakee County, Illinois. Erigenia 11: 1–8.

- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autores y editores de Wikipedia
Cercis canadensis: Brief Summary
(
шпански; кастиљски
)
добавил wikipedia ES
El amor del Canadá o ciclamor del Canadá (Cercis canadensis) es una especie arbórea de la familia de las leguminosas Fabaceae, subfamilia Caesalpinioideae, género Cercis, originaria del este de Norteamérica desde Ontario meridional, Canadá, hacia el sur hasta el norte de Florida, Estados Unidos y el este de México.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autores y editores de Wikipedia
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu
(
фински
)
добавил wikipedia FI
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu[3] eli nuppupuu[4] (Cercis canadensis) on Pohjois-Amerikan itä- ja eteläosista kotoisin oleva kesävihanta pensas tai puu, joka kuuluu juudaksenpuiden sukuun ja hernekasvien heimoon.[2][4] Se on läheistä sukua Välimeren ympäristössä kasvavalle juudaksenpuulle, josta sen erottaa tummanvihreiden lehtien ja pienempien kukkien perusteella.[4] Se on valittu Oklahoman osavaltiopuuksi.[2]
Ulkonäkö ja koko
![src=]()
Amerikanjuudaksenpuun kukkia.
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu on pieni puu tai pensas, jonka korkeus on keskimäärin 8 metriä ja enintään 15 metriä.[2] Sillä on pitkät ja harvat juuret, melko suora runko, tasainen tai pyöreä latvus sekä harittavat haarat, jotka alkavat 1,5–2 metrin korkeudelta puun tyvestä.[2][4][5] Toisin kuin monilla muilla hernekasveilla sillä ei ole juurissaan typpeä sitovia juurinystyröitä.[2] Kaarna on nuorilla puilla sileää ja ruskeaa mutta muuttuu vanhemmiten tummanharmaaksi ja alkaa halkeilla suomumaisina kilpinä. Siinä voi olla myös punaruskeita läiskiä ja oranssinvärisiä halkeamia.[4][5]
Kuluvan vuoden kasvainranka on ohut, polveileva ja lähes musta lukuun ottamatta vaaleita korkkihuokosia. Talvisilmut ovat hyvin pienet ja väriltään tummanpunaiset tai punaruskeat.[5] Lehdet sijaitsevat varrella kierteisesti, ja niiden lehtiruoti on paksu molemmista päistään. Lehtilapa on 8–13 senttimetriä pitkä, lähes pyöreä, ehytlaitainen, lyhytsuippuinen ja herttatyvinen.[4][5] Lehdet ovat vastapuhjenneina pronssinpunaiset mutta muuttuvat vähitellen tummanvihreiksi. Syysväritykseltään ne ovat keltaiset.[4]
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu kukkii maalis–toukokuussa ennen lehtien puhkeamista.[4][6] Sen kaksineuvoiset, perhomaiset herneenkukat ovat perällisiä, tumman- tai vaaleanpunaisia ja noin 1 senttimetrin pituisia. Ne puhkeavat 2–8 kukan ryppäinä suoraan rungosta ja vanhoista haararangoista.[4][5][6] Mehiläisten pölytettyä kukat niiden sikiäimistä kehittyy keskikesään mennessä kuivia palkohedelmiä, jotka ovat 5–10 senttimetriä pitkiä ja ruskeanvärisiä. Palkojen sisälle kypsyy loppukesästä 4–10 kovaa, ruskeaa pavunmuotoista siementä, jotka putoavat maahan syksyn ja talven aikana ja leviävät tuulen ja villieläinten mukana puun ympäristöön.[5][6]
Levinneisyys
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu on kotoisin Pohjois-Amerikan itä- ja eteläosista, ja siitä tunnetaan seuraavat kolme maantieteellistä muunnosta:[2][6][7]
Elinympäristö
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu menestyy parhaiten puolivarjoisilla tai aurinkoisilla paikoilla, kosteassa ja yleensä emäksisessä maaperässä, joka läpäisee hyvin vettä. Yleensä sitä tavataan metsänreunoissa ja kalkkikivikallioilla aina 700 metrin korkeudelle asti paitsi Texasissa, jossa se kasvaa 700–1 500 metrin korkeudessa.[2][6]
Käyttö
Amerikanjuudaksenpuun puuaines on raskasta, kovaa ja tiheäsyistä mutta lujuusominaisuuksiltaan heikkoa. Pienen kokonsa vuoksi sillä ei ole juurikaan merkitystä puuteollisuudelle. Se on kuitenkin suosittu koristepuu Yhdysvaltojen itäosissa ja tärkeä hunajakasvi. Aikaisemmin sen kuoresta on myös valmistettu lääkettä, jolla on hoidettu punatautia. Sen palkoja syövät monet villieläimet, esimerkiksi fasaani, punarintakardinaali, peltoviiriäiset, valkohäntäpeura ja harmaaorava.[2][6]
Lähteet
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedian tekijät ja toimittajat
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu: Brief Summary
(
фински
)
добавил wikipedia FI
Amerikanjuudaksenpuu eli nuppupuu (Cercis canadensis) on Pohjois-Amerikan itä- ja eteläosista kotoisin oleva kesävihanta pensas tai puu, joka kuuluu juudaksenpuiden sukuun ja hernekasvien heimoon. Se on läheistä sukua Välimeren ympäristössä kasvavalle juudaksenpuulle, josta sen erottaa tummanvihreiden lehtien ja pienempien kukkien perusteella. Se on valittu Oklahoman osavaltiopuuksi.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedian tekijät ja toimittajat
Gainier du Canada
(
француски
)
добавил wikipedia FR
Cercis canadensis

Gainier du Canada
Forest Pansy.
Le gainier du Canada ou gainier rouge (Cercis canadensis) est un petit arbre au feuillage caduc originaire d'Amérique du Nord, de la famille des fabacées selon la classification phylogénétique (anciennement de la famille des césalpiniacées). C’est l’arbre de l’État de l’Oklahoma.
Il atteint généralement entre 6 et 9 m de haut avec 8 à 10 mètres d’extension. Il a généralement un court tronc, souvent tordu et des branches étalées. Un arbre de 10 ans sera généralement haut d'environ 5 m. L’écorce est de couleur sombre, lisse. Plus tard, elle devient écailleuse avec une crête un peu apparente, parfois avec des taches marrons. Les rameaux sont minces et en zigzags, presque noirs, parsemés de lenticelles plus légères. Les bourgeons d’hiver sont petits, arrondis et sombres, allant du rouge au marron. Les feuilles sont alternées, simples, et le cœur en forme avec une marge entière. Leurs dimensions sont de 7 à 12 cm de long et large, minces, ressemblant à du papier et parfois légèrement velues dessous.
Variétés
Selon ITIS (19 janvier 2019)[1] :
-
Cercis canadensis var. canadensis L.
-
Cercis canadensis var. mexicana (Rose) M. Hopkins
-
Cercis canadensis var. texensis (S. Watson) M. Hopkins
Références
-
(en) Cet article est partiellement ou en totalité issu de l’article de Wikipédia en anglais intitulé .
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Auteurs et éditeurs de Wikipedia
Gainier du Canada: Brief Summary
(
француски
)
добавил wikipedia FR
Cercis canadensis

Gainier du Canada Forest Pansy.
Le gainier du Canada ou gainier rouge (Cercis canadensis) est un petit arbre au feuillage caduc originaire d'Amérique du Nord, de la famille des fabacées selon la classification phylogénétique (anciennement de la famille des césalpiniacées). C’est l’arbre de l’État de l’Oklahoma.
Il atteint généralement entre 6 et 9 m de haut avec 8 à 10 mètres d’extension. Il a généralement un court tronc, souvent tordu et des branches étalées. Un arbre de 10 ans sera généralement haut d'environ 5 m. L’écorce est de couleur sombre, lisse. Plus tard, elle devient écailleuse avec une crête un peu apparente, parfois avec des taches marrons. Les rameaux sont minces et en zigzags, presque noirs, parsemés de lenticelles plus légères. Les bourgeons d’hiver sont petits, arrondis et sombres, allant du rouge au marron. Les feuilles sont alternées, simples, et le cœur en forme avec une marge entière. Leurs dimensions sont de 7 à 12 cm de long et large, minces, ressemblant à du papier et parfois légèrement velues dessous.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Auteurs et éditeurs de Wikipedia
Cercis canadensis
(
италијански
)
добавил wikipedia IT
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autori e redattori di Wikipedia
Cercis canadensis: Brief Summary
(
италијански
)
добавил wikipedia IT
Cercis canadensis L. è un piccolo arbusto o albero della famiglia delle Fabacee (o Leguminose), nativo del Nord America.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autori e redattori di Wikipedia
Amerikajudastre
(
норвешки
)
добавил wikipedia NO
Amerikajudastre (Cercis canadensis ) er et løvfellende tre i erteblomstfamilien fra østlige Nord-Amerika.
Beskrivelse
Det blir mellom 4 og 10 m høyt. Barken har fine furer. Bladene er enkle, helrandede, håndnervede og avrundede med hjerteformet basis. Blomstene sitter 2–8 sammen på eldre greiner eller på selve stammen (kauliflori). Blomstringen begynner før løvsprett i mars–mai. Blomstene er purpurrosa, mer sjeldent hvite. Begeret er klokkeformet med fem butte tenner og har en mørkere farge. Frukten er en brun, flat belg som er 5–10 cm lang og 1,3 cm bred. Den inneholder 4–10 brune frø som er 6 mm lange.
Økologi
Amerikajudastre vokser som undervegetasjon i mange typer løvskog og finnes også langs elver og i åkerkanter. Pollineringen gjøres av bier. Frøene etes av fasan, nordkrattvaktel, rødkardinal og rosenbrysttykknebb. Hvithalehjort kan beite litt på bladverket.
Nytte
Arten er vanlig plantet i hager i det østlige USA. Trevirket er tungt og hardt, men små dimensjoner og krokete stammer gjør at det ikke har noen økonomisk betydning. Blomstene brukes av og til i salater.
Systematikk og utbredelse
Amerikajudastre i snever forstand, var. canadensis, er utbredt nordover til New Jersey, sørlige Pennsylvania, Ohio, sørlige Ontario, Michigan, Illinois, Iowa og Nebraska. Vestgrensa går igjennom Kansas og nordlige Oklahoma. Den mangler stort sett på kystslettene i øst og sør, men det er noen spredte forekomster så langt sør som i Louisiana og sentrale Florida.
En annen varietet, var. texensis, finnes i sørlige Oklahoma og Texas øst for Pecos. Den ble tidligere noen ganger skilt ut som en egen art, Cercis reniformis. En tredje varietet, var. mexicana, finnes i Trans-Pecos og videre sørover i Mexico. Den ble tidligere regnet som arten Cercis mexicana. Molekylærgenetiske studier viser at alle tre varieteter er nært beslektet og bør regnes til samme art.
Galleri
Litteratur
- J.G. Dickson. «Eastern Redbud». Silvics of North America. Besøkt 27. desember 2018.
- «Redbud». Illinois Wildflowers. Besøkt 27. desember 2018.
- P.W. Fritsch og B.C. Cruz (2012). «Phylogeny of Cercis based on DNA sequences of nuclear ITS and four plastid regions: implications for transatlantic historical biogeography». Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 62 (3): 816–825. ISSN 1055-7903. PMID 22142738. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2011.11.016.
Eksterne lenker
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia forfattere og redaktører
Amerikajudastre: Brief Summary
(
норвешки
)
добавил wikipedia NO
Amerikajudastre (Cercis canadensis ) er et løvfellende tre i erteblomstfamilien fra østlige Nord-Amerika.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia forfattere og redaktører
Judaszowiec kanadyjski
(
полски
)
добавил wikipedia POL
 Multimedia w Wikimedia Commons
Multimedia w Wikimedia Commons Judaszowiec kanadyjski (Cercis canadensis L.) – gatunek drzewa z rodziny bobowatych (Fabaceae), z plemienia Cercideae. Występuje w Ameryce Północnej, na terenie Stanów Zjednoczonych w pasie od Nowego Jorku po Teksas[4]. Jest chętnie uprawiany jako roślina ozdobna.
Morfologia
- Pokrój
- Małe drzewo o rozłożystej i szerokiej koronie, dorastające 10 m wysokości[4].
- Kora
- Charakterystyczna o ciemnopopielatej barwie, miejscami niemal czarna[4].
- Liście
- Sercowate, zaokrąglone, całobrzegie do 10 cm długości i 13 cm szerokości. Początkowo brązowozielone, po rozwinięciu zmieniają barwę na jasnozieloną. Jesienią żółkną i przybierają złocisty kolor. Blaszki gładkie i bardzo cienkie[4].
- Kwiaty
- Małe, różowe kwiaty motylkowe o średnicy około 1 cm, rosnące w pęczkach. Wyrastają obficie na starych pędach i bezpośrednio z pnia. [4].
- Owoce
- Spłaszczony, zielony (z czasem brązowiejący) strąk[4].
Biologia i ekologia
Fanerofit. Roślina jednopienna, owadopylna. Kwitnie wiosną i wczesnym latem. Rośnie w wilgotnych lasach południowego wschodu Stanów Zjednoczonych. Wykazuje podatność na raka, powodującego usychanie liści latem[4]. Młode osobniki rosną powoli i są wrażliwe na mrozy[5].
Zagrożenia i ochrona
Gatunek ten wpisany jest do Czerwonej księgi gatunków zagrożonych w kategorii gatunek najmniejszej troski (ang. Least Concern – LC)[3].
Zastosowanie
- Roślina ozdobna
- Drzewo chętnie sadzone w parkach, w ogrodach oraz wzdłuż ulic. Na jego bazie wyhodowano kultywar 'Forest Pansy', o intensywnie purpurowoczerwonych liściach[4].
Przypisy
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autorzy i redaktorzy Wikipedii
Judaszowiec kanadyjski: Brief Summary
(
полски
)
добавил wikipedia POL
Judaszowiec kanadyjski (Cercis canadensis L.) – gatunek drzewa z rodziny bobowatych (Fabaceae), z plemienia Cercideae. Występuje w Ameryce Północnej, na terenie Stanów Zjednoczonych w pasie od Nowego Jorku po Teksas. Jest chętnie uprawiany jako roślina ozdobna.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Autorzy i redaktorzy Wikipedii
Amerikanskt judasträd
(
шведски
)
добавил wikipedia SV
Amerikanskt judasträd (Cercis canadensis) art i familjen ärtväxter och förekommer naturligt i centrala och östra USA och söderut till Mexiko. Arten odlas ibland som trädgårdsväxt i sydligaste Sverige.
Underarter
Arten är mångformig och tre underarter kan urskiljas.
- subsp. canadensis - Har tunna, vanligen spetsiga blad, om rundade så är de mer än 7 cm långa. Förekommer i östra Nordamerika.
- subsp. mexicana - är mindre och än mer anpassad till torra platser än subsp. textensis och har än mer vågiga bladkanter. Räknas ibland in under subsp. texensis. Förekommer i Texas och nordöstra Mexiko.
- subsp. texensis - är mindre och mer tolktolerant än huvudunderarten. Bladen är läderartade, har vanligen rundad spets vågiga kanter. Är bladen spetsiga blir de aldrig längre än 7 cm. Förekommer i Oklahoma, Texas och nordöstra Mexiko.
Sorter
Inom trädgårdsodlingen förekommer ett flertal sorter:[1][2]
- 'Alba' (syn. var. alba) - (subsp. canadensis) har vita blommor. Frökonstant. Säljs ibland felaktigt som 'Texas White'.
- 'Ace of Hearts' - (subsp. canadensis) - kompakt sort som blir cirka 3 m hög. Ljust purpurrosa blommor.
- 'Appalachian Red' - har djupt purpurröda knoppar som slår ut till klart rosa blommor. Blir cirka 6–10 m hög.
- 'Cascading Hearts' - (subsp. canadensis) har hängande grenar och mindre blad än arten i övrigt. 2–4 m hög.
- 'Convey' (syn. 'Lavender Twist') - (subsp. canadensis) har förvridna, hängande grenar och purpurrosa blommor. Blir cirka 1,5 m hög eller högre om den binds upp.
- 'Dwarf White' - blir endast 2,5–3 m hög. Blommorna är vita. Rikblommande.
- 'Flame' (syn. 'Plena') - fylldblommig med purpurrosa blommor. Blommar relativt sent och sätter sällan frukt. Snabbväxande.
- 'Forest Pansy' - (subsp. canadensis) nya blad är purpurröda, de blir senare mer dovt purpur eller purpurgröna. Blommar relativt sent med purpurrosa blommor.
- 'Oklahoma' - (subsp. texensis) mycket rikblommande med mörkt purpur blommor. 4–8 m hög.
- 'Royal White' - har vita blommor. Mer härdig än ‘Alba’, med större blommor som slår ut tidigare.
- 'Silver Cloud' - har vitfläckiga blad och purpurrosa blommor. Föredrar halvskugga.
- 'Tennessee Pink' - har klart rosa blommor. Blir cirka 6 m hög.
- 'Texas White' - är en vitblommig sort av subsp. texensis.
- 'Traveler' - (subsp. texensis) - sorten har hängande grenar, 1,8–2 m hög.
- 'Winthers Pink Charm' - har mjukt rosa blommor utan purpur inslag.
Synonymer
[3][4]
subsp. canadensis
-
Cercis canadensis f. alba Rehder = 'Alba'
-
Cercis canadensis f. glabrifolia Fernald
-
Cercis canadensis var. alba (Rehder) Bean = 'Alba'
-
Cercis canadensis var. plena Sudw. = 'Flame'
-
Cercis canadensis var. pubescens Pursh
-
Cercis canadensis var. typica M.Hopkins
-
Cercis dilatata Greene
-
Cercis ellipsoidea Greene
-
Cercis georgiana Greene
-
Siliquastrum canadense (L.) Medik.
-
Siliquastrum cordatum Moench
subsp. mexicana (Rose) A.E.Murray
-
Cercis canadensis var. mexicana (Rose) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis mexicana Rose
subsp. texensis S.Watson) A.E.Murray
-
Cercis canadensis var. texensis S.Watson) M.Hopkins
-
Cercis nitida Greene
-
Cercis occidentalis var. texensis S.Watson
-
Cercis reniformis Engelm. ex A.Gray
-
Cercis texensis (S.Watson) Sarg.
Referenser
-
^ NC State University - Cercis canadensis cultivars
-
^ Elm Nursery/Commercial Nursery Arkiverad 8 maj 2008 hämtat från the Wayback Machine.
-
^ ILDIS International Legume Database & Information Service Arkiverad 17 maj 2014 hämtat från the Wayback Machine.
-
^ International Plant Names Index
Externa länkar
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia författare och redaktörer
Amerikanskt judasträd: Brief Summary
(
шведски
)
добавил wikipedia SV
Amerikanskt judasträd (Cercis canadensis) art i familjen ärtväxter och förekommer naturligt i centrala och östra USA och söderut till Mexiko. Arten odlas ibland som trädgårdsväxt i sydligaste Sverige.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia författare och redaktörer
Церцис канадський
(
украински
)
добавил wikipedia UK
Поширення та середовище
У природі ареал виду охоплює Північну Америку — від Нью-Йорка на південь до Флориди та на захід до Айови, Небраски, Техасу і півночі Мексики.
У культурі поширений на Чорноморському узбережжі Кавказу, росте і плодоносе у Баку, Єревані, Тбілісі, в Україні (в Ужгороді, Києві), а також в Середній Азії.
Дещо теплолюбний. Досить вимогливий до вологості та поживності грунту. Страждає від посухи.
Будова
Дерево заввишки до 18 м з шатровидною кроною. Гілки та стовбур з чорно-сірою корою. Пагони червоні.
Листя широкі яйцеподібні до майже округлих, довжиною (5)8—16 см, з серцеподібною основою і короткозагоостренною верхівкою, опушені зазвичай лише знизу, біля основи пластинки, зверху сизо-зелені, знизу тьмяно-сизі, восени світло-жовті.
Квітки по 4—8 в пучках, світло-рожеві або рожево-лілуваті, довжиною 1—1,2 см.
Боби довжиною 6—10 см, шириною 2 см. Насіння овальне, довжиною 5—6 мм, шириною 4-5 мм, матові, темно-коричневі. Вага 1 тис. насіннин 20—30 г
Цвіте в квітні — травні. Плодоносить у вересні - жовтні.
Класифікація
Різновиди
В рамках виду виділяють три різновиди:
-
Cercis canadensis var. canadensis
-
Cercis canadensis var. mexicana
-
Cercis canadensis var. texensis
На цю статтю не посилаються інші статті Вікіпедії.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Автори та редактори Вікіпедії
Cercis canadensis
(
виетнамски
)
добавил wikipedia VI
Cercis canadensis là một loài thực vật có hoa trong họ Đậu. Loài này được L. miêu tả khoa học đầu tiên.[2]
Hình ảnh
Chú thích
Liên kết ngoài
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia tác giả và biên tập viên
Cercis canadensis: Brief Summary
(
виетнамски
)
добавил wikipedia VI
Cercis canadensis là một loài thực vật có hoa trong họ Đậu. Loài này được L. miêu tả khoa học đầu tiên.
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Wikipedia tác giả và biên tập viên
Багрянник канадский
(
руски
)
добавил wikipedia русскую Википедию
Эта статья — о виде растений Cercis canadensis рода Cercis семейства Бобовые. О растениях рода Cercidiphyllum семейства Багрянниковые, иногда называемых «багрянниками», см.
Церцидифиллюм.
Вид: Багрянник канадский
Международное научное название
Cercis canadensis L.
Ареал 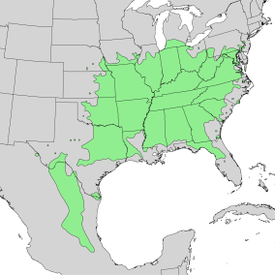
Охранный статус  Систематика
Систематика
на Викивидах Изображения
Изображения
на Викискладе ITIS 25782NCBI 49801EOL 640323GRIN t:300123IPNI 485668-1TPL ild-20153 Багрянник канадский[2], или Церцис канадский (лат. Cercis canadensis) — деревья, вид рода Церцис (Cercis) семейства Бобовые (Fabaceae).
Распространение и экология
В природе ареал вида охватывает Северную Америку — от Нью-Йорка на юг до Флориды и на запад до Айовы, Небраски, Техаса и севера Мексики.
В культуре распространён на Черноморском побережье Кавказа на юг от Сочи, растет и плодоносит в Баку, Ереване, Тбилиси, на Украине (в Ужгороде, Киеве), а также в Средней Азии[3].
Относительно теплолюбив. Довольно требователен к влажности и богатству почвы. Страдает от засухи[3].
Биологическое описание
Дерево высотой до 18 м с шатровидной кроной. Ветви и ствол с чёрно-серой корой. Побеги красные.
Листья широкояйцевидные до почти округлых, длиной (5) 8—16 см, с сердцевидным основанием и короткозаострённой верхушкой, опушённые обычно лишь снизу, близ основания пластинки, сверху сизо-зелёные, снизу тускло-сизоватые, осенью светло-жёлтые.
Цветки по 4—8 в пучках, светло-розовые или розово-лиловатые, длиной 1—1,2 см.
Бобы длиной 6—10 см, шириной 2 см. Семена овальные, длиной 5—6 мм, шириной 4—5 мм, матовые, тёмно-коричневые. Вес 1 тыс. семян 20—30 г.
Цветёт в апреле — мае. Плодоносит в сентябре — октябре.
Слева направо:
Листья. Листья в осенней окраске. Бутоны. Цветки.
Классификация
Разновидности
В рамках вида выделяют три разновидности:[4]
Таксономия
Вид Церцис канадский входит в род Церцис (Cercis) трибы Багряниковые (Cercideae) подсемейства Цезальпиниевые (Caesalpinioideae) семейства Бобовые (Fabaceae) порядка Бобовоцветные (Fabales).
ещё 3 семейства
(согласно
Системе APG II) ещё 3 трибы
(согласно
Системе APG II) ещё от 5 до 9 видов порядок
Бобовоцветные подсемейство
Цезальпиниевые род
Церцис отдел
Цветковые, или Покрытосеменные семейство
Бобовые триба
Багряниковые вид
Церцис канадский ещё 44 порядка цветковых растений
(согласно
Системе APG II) ещё 2 подсемейства
(согласно
Системе APG II) ещё 5 родов
Примечания
-
↑ Об условности указания класса двудольных в качестве вышестоящего таксона для описываемой в данной статье группы растений см. раздел «Системы APG» статьи «Двудольные».
-
↑ Русское название таксона — согласно следующему изданию:
- Шрётер А. И., Панасюк В. А. Словарь названий растений = Dictionary of Plant Names / Межд. союз биол. наук, Нац. к-т биологов России, Всерос. ин-т лек. и ароматич. растений Рос. сельскохоз. академии; Под ред. проф. В. А. Быкова. — Koenigstein: Koeltz Scientific Books, 1999. — С. 172. — 1033 с. — ISBN 3-87429-398-X.
-
↑ 1 2 Лапин П. И., Калуцкий К. К., Калуцкая О. Н. Интродукция лесных пород. — М: Лесн. пром-сть, 1979. — С. 132—133. — 224 с. — 2200 экз.
-
↑ По данным сайта GRIN (см. карточку растения).
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Авторы и редакторы Википедии
Багрянник канадский: Brief Summary
(
руски
)
добавил wikipedia русскую Википедию
Багрянник канадский, или Церцис канадский (лат. Cercis canadensis) — деревья, вид рода Церцис (Cercis) семейства Бобовые (Fabaceae).
- лиценца
- cc-by-sa-3.0
- авторски права
- Авторы и редакторы Википедии
加拿大紫荊
(
кинески
)
добавил wikipedia 中文维基百科
二名法 Cercis canadensisL. 加拿大紫荊,是豆科紫荊屬的一種大型灌木或小喬木,原產於北美洲東部,從加拿大安大略省南部往南至美國佛羅里達州北部。因為原生於美國東部地區且具有紅色的花苞,在美國稱為Eastern Redbud(東部紫荊)。
形態特徵
株高6-9公尺,樹冠寬8-10公尺,樹齡十年的樹大約可以長到5公尺高。樹皮紅褐色,裂開呈鱗片狀。樹枝細長,起初為亮褐色,後來變為暗褐色,枝上的皮孔顏色較淡呈斑點狀。冬芽細小,圓形,顏色為暗紅色至栗褐色。葉單葉,互生,葉心形,葉緣全緣。葉長及寬約7-12公分,葉薄,紙質,葉背略有毛。花色艶麗,淡至深紫粉紅色。花長1.5公分,三至五月開花,先開花後長葉。花由具有長舌的昆蟲——如藍莓蜂或木蜂——幫忙授粉,短舌的蜂類由於舌頭太短接觸不到蜜腺。果實為扁平狀的乾果,褐色。果莢似豌豆莢,長5-10公分。果莢內生有種子,種子褐色,扁橢圓形,種子長0.6公分,於八至十月時成熟。
用途
在野外,加拿大紫荊是混合林內常見的林下原生樹種。花色艷麗常種植作為一個園林觀賞樹木。葉子是某些鱗翅目昆蟲幼蟲的食草。
在阿巴拉契亞南部的某些地區,烹煮鹿肉或負鼠肉等野味時,會以加拿大紫荊的嫩枝作為調味料。正因為如此,在這些山區有時也稱加拿大紫荊為山胡椒樹(Spicewood tree)。
美洲原住民會食用加拿大紫荊的花及種子,花朶生吃或經煮過才吃,種子食用前會先烤過。花的提取物含有花青素,發育中的綠色種子含有原花青素,種子中含有亞麻酸,α-亞麻酸,油酸和棕櫚酸。[2]
象徵
加拿大紫荊是美國奧克拉荷馬州的州樹。
參考資料
加拿大紫荊: Brief Summary
(
кинески
)
добавил wikipedia 中文维基百科
加拿大紫荊,是豆科紫荊屬的一種大型灌木或小喬木,原產於北美洲東部,從加拿大安大略省南部往南至美國佛羅里達州北部。因為原生於美國東部地區且具有紅色的花苞,在美國稱為Eastern Redbud(東部紫荊)。


 Esta páxina forma parte del wikiproyeutu Botánica, un esfuerciu collaborativu col fin d'ameyorar y organizar tolos conteníos rellacionaos con esti tema. Visita la páxina d'alderique del proyeutu pa collaborar y facer entrugues o suxerencies.
Esta páxina forma parte del wikiproyeutu Botánica, un esfuerciu collaborativu col fin d'ameyorar y organizar tolos conteníos rellacionaos con esti tema. Visita la páxina d'alderique del proyeutu pa collaborar y facer entrugues o suxerencies. 
 Gainier du Canada Forest Pansy.
Gainier du Canada Forest Pansy.