mk
имиња во трошки

Caulimoviridae és una família de virus d'ADN bicatenari amb retrotranscripció. Són virus de les plantes.
Caulimoviridae és una família de virus d'ADN bicatenari amb retrotranscripció. Són virus de les plantes.
Als Caulimoviridae bezeichnet man eine Familie von Pararetroviren, die vor allem Pflanzen schädigen. Die Vertreter der Caulimoviridae lassen sich in zwei Gattungen aufteilen: Die Gattung Caulimovirus weist eine ikosaedrische Symmetrie ihrer Proteinhülle (Kapsid) auf. Im Unterschied dazu sind die Vertreter der Gattung Badnavirus in ihrer Form bazillenähnlich (bazilliform), das heißt stäbchenförmig, aufgebaut. Vertreter dieser Familie sind für bei Kulturpflanzen wirtschaftlich bedeutsame Viruserkrankungen verantwortlich. So ist der Tungrovirus als einer der Badnaviren der Verursacher schwerer Epidemien bei Reis (Oryza sativa), die weltweit für hohe Ertragseinbußen verantwortlich sind. Weitere durch Vertreter der Caulimoviridae geschädigte Kulturpflanzen sind beispielsweise Zuckerrohr, Kakaobäume oder Bananen.
Die Vertreter der Caulimoviridae lassen sich in zwei größere Gruppen aufteilen, die sich morphologisch unterscheiden: Die Vertreter der Gattung Caulimovirus weisen eine dreischichtige Proteinhülle (Kapsid) mit ikosaedrischer Symmetrie auf. Die so gestaltete Hülle umgibt einen Innenraum von etwa 25 nm Durchmesser.
Die Vertreter der Badnavirus-Gruppe hingegen haben eine bazillenähnliche Struktur und sind stäbchenförmig geformt. Ihre Länge kann zwischen 60 und 900 nm variieren, beträgt aber im Schnitt 130 nm bei einem Durchmesser von 90 nm. Auch die Struktur der Badnaviren basiert auf einer ikosaedrischen Symmetrie.
Auch bei der Genomorganisation setzen sich die Unterschiede zwischen den beiden genannten Hauptgruppen fort. Gemeinsam ist allen Vertretern eine doppelsträngige DNA (dsDNA) mit etwa 7000 bis 8000 Basenpaaren. Das Genom der Caulimoviren besteht aus einem Molekül einer doppelsträngigen dsDNA von 7,2 bis 8,2 kbp, die in den Viruspartikel offen zirkulär vorliegt. Das Genom des Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) enthält dabei sieben so genannte Offene Leserahmen (ORF), Petunia vein clearing virus-like nur zwei ORF. Bei der Gattung Badnavirus und ihrer Typusspezies, dem Commelina yellow mottle virus (ComYMV), liegt das Genom ebenfalls als zirkuläre dsDNA mit 7,5 kbp und drei ORF vor. Nach dem erfolgreichen Eintritt in den Wirtsorganismus muss das virale dsDNA-Genom der Caulimoviridae mit Hilfe einer reversen Transkriptase in RNA transkribiert werden. Dies läuft bei den genannten Vertretern beider Gruppen nach dem gleichen Muster ab.
Bei dem Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) und wahrscheinlich anderen Caulimoviren spielen Blattläuse, speziell die Grüne Pfirsichblattlaus (Myzus persicae) und die Blumenkohllaus (Brevycorine brassicae) eine große Rolle als tierische Vektoren. Bei Badnaviren spielen auch Zwergzikaden oder Schildläuse eine Rolle als Überträgertiere. Die Übertragung erfolgt dabei semipersistent und nicht zirkulativ. Weitere Ausbreitungsmöglichkeiten sind durch die gängigen Methoden der generativen und vegetativen Vermehrung wie Samenaussaat oder Stecklingsvermehrung gegeben.
Als Caulimoviridae bezeichnet man eine Familie von Pararetroviren, die vor allem Pflanzen schädigen. Die Vertreter der Caulimoviridae lassen sich in zwei Gattungen aufteilen: Die Gattung Caulimovirus weist eine ikosaedrische Symmetrie ihrer Proteinhülle (Kapsid) auf. Im Unterschied dazu sind die Vertreter der Gattung Badnavirus in ihrer Form bazillenähnlich (bazilliform), das heißt stäbchenförmig, aufgebaut. Vertreter dieser Familie sind für bei Kulturpflanzen wirtschaftlich bedeutsame Viruserkrankungen verantwortlich. So ist der Tungrovirus als einer der Badnaviren der Verursacher schwerer Epidemien bei Reis (Oryza sativa), die weltweit für hohe Ertragseinbußen verantwortlich sind. Weitere durch Vertreter der Caulimoviridae geschädigte Kulturpflanzen sind beispielsweise Zuckerrohr, Kakaobäume oder Bananen.
Caulimoviridae is a family of viruses infecting plants.[1] There are 94 species in this family, assigned to 11 genera.[2][3] Viruses belonging to the family Caulimoviridae are termed double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) reverse-transcribing viruses (or pararetroviruses) i.e. viruses that contain a reverse transcription stage in their replication cycle. This family contains all plant viruses with a dsDNA genome that have a reverse transcribing phase in their lifecycle.
The following genera are recognized:[3]
All viruses of this family are non-enveloped. Virus particles are either bacilliform or isometric. The type of nucleocapsid incorporated into the virus structure determines the size of the viral particles. Bacilliform particles are approximately 35–50 nm in diameter and up to 900 nm in length. Isometric particles are on average 45–50 nm in diameter and show icosahedral symmetry.
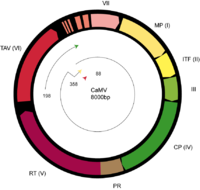
The genomes of viruses from this family contain monopartite, non-covalently closed circular dsDNA of 7.2–9.3 kbp with discontinuities in both genome strands at specific places. These genomes contain one open reading frame (ORF), as observed in petuviruses, to eight ORFs such as in the soymoviruses. Proteins encoded by the viral genomes include reverse transcriptase-ribonuclease H, aspartic proteases, nucleocapsids and transactivators — there are other proteins essential for replication that have yet to be assigned a specific function.
Replication takes place in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus of host cells. Firstly, the viral genome enters the cytoplasm. The viral DNA forms supercoiled mini-chromosome structures upon entering the host nucleus, where it is transcribed into polyadenylated RNA which is terminally redundant (due to transcription occurring twice for some parts of the DNA). Newly transcribed RNA enters the cytoplasm where it is either translated into viral proteins, or retrotranscribed into new copies of the dsDNA viral genome by the viral reverse transcriptase. New dsDNA genomes are encapsidated in the cytoplasm and released.
The replication process involves a retro transcription step and an RNA intermediate, therefore viruses from the family Caulimoviridae are not considered true dsDNA viruses — instead they are termed DNA reverse-transcribing viruses. They share this characteristic with retroviruses. However, unlike retroviruses, viruses from the family Caulimoviridae do not require the integration of the viral genome into the genome of their hosts in order to replicate and for this reason their genome does not encode the enzymatic protein integrase.
The presence of endogenous viral elements (EVEs) in plant genomes is widespread.[4][5][6] and most known plant EVEs originate from viruses with DNA genomes in the family Caulimoviridae. Integration is thought to occur through non-homologous end-joining (illegitimate recombination) during DNA repair mechanisms. Most plant EVEs are non infectious. However, infectious Caulimoviridae EVEs have been reported in the genome of petunia [7](Petunia vein clearing virus), banana [8](Banana streak OL virus, Banana streak GF virus, Banana streak IM virus) and Nicotiana edwardsonii [9](Tobacco vein clearing virus).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) Caulimoviridae is a family of viruses infecting plants. There are 94 species in this family, assigned to 11 genera. Viruses belonging to the family Caulimoviridae are termed double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) reverse-transcribing viruses (or pararetroviruses) i.e. viruses that contain a reverse transcription stage in their replication cycle. This family contains all plant viruses with a dsDNA genome that have a reverse transcribing phase in their lifecycle.
Caulimoviridae es una familia de virus ADN retrotranscritos que infectan plantas. Su genoma consiste en una cadena de ADN bicatenario, por tanto, se incluyen en el Grupo VII de la Clasificación de Baltimore.
Todos los virus de esta familia no presentan envoltura. Las partículas del virus contienen una nucleocápside de dos posibles formas: baciliforme o isométrica. El tipo de nucleocápside incorporado en la estructura del virus determina el tamaño de los virus. La nucleocápside de los virus baciliformes mide unos 35-50 nm de diámetro y llega hasta 900 nm de longitud. Los virus de nucleocápside isométrica miden, en promedio, 45-50 nm de diámetro y muestran simetría icosaédrica.
La familia incluye los siguientes géneros:
El genoma de los virus de esta familia consiste en un único segmento de ADN, ya sea de estructura circular o lineal. El tamaño del genoma es usualmente de 6.000-8.000 pares de bases. Dependiendo del virus, el ADN puede contener un marco abierto de lectura (ORF), como por ejemplo en Pertuvirus, o hasta ocho ORFs como en Soyamovirus. Las proteínas codificadas en el genoma de esta familia incluyen la transcriptasa inversa, proteasas, la nucleocápside y transactivadores. Hay otras proteínas esenciales para la replicación a las que aún no se le ha asignado una función específica.
La replicación se lleva a cabo tanto en el citoplasma como en el núcleo de la célula huésped. En primer lugar, el ADN viral entra en el citoplasma donde forma estructuras mini-cromosómicas altamente empaquetadas que, a continuación, entran en el núcleo de la célula huésped. El ADN viral se transcribe en ARN con poliadenilación que es terminalmente redundante debido a que la transcripción se produce dos veces para algunas partes del ADN. El ARN transcrito entra nuevamente en el citoplasma, en donde puede realizar dos funciones. Puede utilizarse como plantilla para la síntesis de las proteínas virales o puede someterse a la transcripción inversa por la transcriptasa inversa codificada por el virus para fabricar ADN monocatenario. Este ADN puede entonces volver a introducirse el núcleo para repetir el proceso (amplificación).
Puesto que la replicación requiere de ARN intermedio, los virus de la familia Caulimoviridae no son verdaderos virus ADN bicatenarios. En lugar de ello se consideran virus ADN bicatenarios retrotranscritos esto es, virus que comprenden una etapa de transcripción inversa en su ciclo de replicación. Esta característica se da también en los retrovirus, sin embargo, existen varias diferencias importantes. Los virus de la familia Caulimoviridae, a diferencia de los retrovirus, no requieren la integración viral en el genoma del huésped con el fin de replicarse y por esta razón su genoma no codifica la proteína enzimática integrasa.
Caulimoviridae es una familia de virus ADN retrotranscritos que infectan plantas. Su genoma consiste en una cadena de ADN bicatenario, por tanto, se incluyen en el Grupo VII de la Clasificación de Baltimore.
Todos los virus de esta familia no presentan envoltura. Las partículas del virus contienen una nucleocápside de dos posibles formas: baciliforme o isométrica. El tipo de nucleocápside incorporado en la estructura del virus determina el tamaño de los virus. La nucleocápside de los virus baciliformes mide unos 35-50 nm de diámetro y llega hasta 900 nm de longitud. Los virus de nucleocápside isométrica miden, en promedio, 45-50 nm de diámetro y muestran simetría icosaédrica.
La familia incluye los siguientes géneros:
Género Badnavirus; especie tipo: Virus del moteado amarillo de Commelina. Género Caulimovirus; especie tipo: Virus del mosaico de la coliflor. Género Tungrovirus; especie tipo: Virus baciliforme del tungro del arroz. Género Soymovirus; especie tipo: Virus del moteado clorótico de la soja. Género Cavemovirus; especie tipo: Virus del mosaico veteado de la yuca. Género Petuvirus; especie tipo: Virus del veteado claro de la petunia.Les Caulimoviridae sont une famille de virus de l'ordre des Ortervirales qui comprend dix genres et 85 espèces. Ce sont des virus à ADN double brin non enveloppés qui ont une phase de transcription inverse dans leur cycle de vie (pararétrovirus). Ils sont classés dans le groupe VII de la classification Baltimore.
Ce sont des phytovirus qui infectent une vaste gamme de plantes monocotylédones et dicotylédones. Certains virus provoquent des maladies économiquement importantes dans les cultures des régions tropicales et subtropicales. La transmission se fait par des insectes-vecteurs, dont des Aphidoidea (pucerons), Coccoidea (cochenilles), Cicadellidae (cicadelles), Tingidae (tigres), et par greffage[3]. C'est la seule famille de virus végétaux possédant un génome d'ADN à double brin.
La plupart des virus endogènes de la famille des Caulimoviridae ne sont pas infectieux, cependant l'activation des éléments viraux endogènes infectieux se produit chez certaines espèces de plantes, notamment Musa balbisiana, Petunia hybrida et Nicotiana edwardsonii[3].
Selon ICTV[2] :
Les Caulimoviridae sont une famille de virus de l'ordre des Ortervirales qui comprend dix genres et 85 espèces. Ce sont des virus à ADN double brin non enveloppés qui ont une phase de transcription inverse dans leur cycle de vie (pararétrovirus). Ils sont classés dans le groupe VII de la classification Baltimore.
Ce sont des phytovirus qui infectent une vaste gamme de plantes monocotylédones et dicotylédones. Certains virus provoquent des maladies économiquement importantes dans les cultures des régions tropicales et subtropicales. La transmission se fait par des insectes-vecteurs, dont des Aphidoidea (pucerons), Coccoidea (cochenilles), Cicadellidae (cicadelles), Tingidae (tigres), et par greffage. C'est la seule famille de virus végétaux possédant un génome d'ADN à double brin.
La plupart des virus endogènes de la famille des Caulimoviridae ne sont pas infectieux, cependant l'activation des éléments viraux endogènes infectieux se produit chez certaines espèces de plantes, notamment Musa balbisiana, Petunia hybrida et Nicotiana edwardsonii.
Caulimoviridae è una famiglia di virus che infettano le piante. Ci sono attualmente 85 specie in questa famiglia, divise tra 10 generi.[1] I virus appartenenti alla famiglia dei Caulimoviridae sono definiti virus a doppio filamento (dsDNA) (o pararetrovirus), ovvero virus che contengono uno stadio di trascrizione inversa nel loro ciclo di replicazione. Questa famiglia contiene tutti i virus delle piante con un genoma dsDNA che ha una fase di trascrizione inversa nel suo ciclo di vita.
Caulimoviridae è una famiglia di virus che infettano le piante. Ci sono attualmente 85 specie in questa famiglia, divise tra 10 generi. I virus appartenenti alla famiglia dei Caulimoviridae sono definiti virus a doppio filamento (dsDNA) (o pararetrovirus), ovvero virus che contengono uno stadio di trascrizione inversa nel loro ciclo di replicazione. Questa famiglia contiene tutti i virus delle piante con un genoma dsDNA che ha una fase di trascrizione inversa nel suo ciclo di vita.
Прості віруси. Капсиди мають ікосаедричну симетрію, трохи витягнуті, інколи мають циліндричну форму. Діаметр 35-50 нм, довжина циліндричних форм 130 нм.
Плавуча густина в CsCl 1.3-1.312-1.4 г см-3. Коефіцієнт седиментації 200-251-285 S20w.
Віріони мають єдину циркулярну длДНК (7.2-8.3 kbp). Кожен ланцюг має розриви у специфічних позиціях, перший має один розрив, другий — 1-3. Організація геному специфічна для роду і є одним з класифікаційних критеріїв. Після потрапляння в клітини розриви зшиваються, утворюючи мініхромосоми. Вони асиметрично транскрибуються РНК-полімеразами господара, утворюючи транскрипт, довший за геном вірусу (35S або 34S РНК), які подовжені на 35-270 нуклеотидів, залежно від виду. Цей транскрипт слугує одночасно матрицею для зворотної транскрипції (-) ДНК, і для деяких ORF. Види роду Caulimovirus продукують специфічну мРНК (19S РНК) для ORF6; ніяких сгРНК не було знайдено у представників Petuvirus, Soymovirus, Cavemovirus and Badnavirus.
Реплікативний цикл проходить у епісомальній формі, без інтеграції. Синтез (-) ДНК починається цитоплазматичною тРНКmet господара. Розриви у ланцюгах — це праймерні ділянки для синтезу ДНК та утворюються внаслідок незшивання ланцюгів.
Білки складають 83-84,41-85,9% від маси віріону. Віріон складається з 1 або 3 структурних білків. Серед неструктурних білків геном кодує РНК-залежну ДНК-полімеразу.
Ліпіди і вуглеводи не виявлені.
Віріони є імуногенами середньої сили. Існує певна антигенна варіабельність серед представників роду Badnavirus.
Коло господарів вузьке.
Представники родів Petuvirus, Soymovirus and Cavemovirus інфікують дводольних; види роду Tungrovirus — однодольних, а роду Badnavirus — або дво-, або однодольних.
Можуть передаватися векторно або при механічних пошкодженнях, при щепленні, насінням, або пилком. Можуть передаватися комахами ряду Hemiptera, родинами Aleyrodidae, Aphididae, Cicadellidae, Pseudococcidae. В переносниках не розмножуються. Багато вірусів поширюються під час вегетативного розмноження.
Віруси широкорозповсюджені; види родів Tungrovirus та Badnavirus переважно існують у тропічних та субтропічних умовах, хоча деякі з них існують у помірних та субарктичних умовах. Види родів Petuvirus, Caulimovirus, Soymovirus та Cavemovirus можна знайти в помірних регіонах.
Симптоматика залежить від регіону і господара. Представники родів Petuvirus, Caulimovirus, Soymovirus and Cavemovirus зазвичай викликають мозаїку, в той час як представники родів Tungrovirus та Badnavirus викликають хлоротичні зміни в листках.
Майже всі види інфікують всі клітини господаря, хоча деякі Tungrovirus та Badnavirus прив'язані до судинної системи. Віріони представників родів Petuvirus, Caulimovirus, Soymovirus та Cavemovirus асоційовані з цитоплазматичними білковими включеннями.
Caulimoviridae
Группа по БалтиморуVII: дцДНК-ОТ-вирусы
Колимовирусы[2] (лат. Caulimoviridae) — семейство ДНК-содержащих вирусов растений с механизмом обратной транскрипции и двуцепочечной ДНК, то есть вирусов, содержащих стадию обратной транскрипции в своём репликативном цикле.
Вирион является простым, без липидной оболочки. Морфология нуклеокапсида представлена 2 основными формами: палочковидной и икосаэдрической. Форма нуклеокапсида зависит от размера вируса. Вирионы палочковидной формы имеют диаметр приблизительно 35—50 нм и могут быть в длину до 900 нм. Икосаэдрический капсид имеет диаметр 45—50 нм и примерно такую же длину.
Геном данного вируса представляет собой несегментированную линейную или циклическую двуцепочечную ДНК. Размер генома насчитывает приблизительно 6—8 kbs. В зависимости от вируса геном может иметь либо одну открытую рамку считывания (ORF), как например у Petuvirus, или больше восьми как у Soymovirus. Геном данного вирусного семейства кодирует такие белки: обратная транскриптаза, протеаза, структурные белки, а также остальные белки с неизвестными функциями, но так или иначе нужные для репликации вируса.
Репликация происходит как в цитоплазме, так и в ядре клетки-хозяина. Сначала, вирусный геном попадает в цитоплазму. Там он формирует суперскрученную минихромосому. На ней транскибируется мРНК вируса, которая избыточна (потому что в некоторые части генома експресируются дважды). Эта транскибируемая РНК попадает в цитоплазму, где она играет две роли. Она может использоваться либо как шаблон для трансляции вирусных белков, либо подвергаться обратной транскрипции до дцДНК, с помощью вирусной ревертазы. Так как эти вирусы имеют много общего с ретровирусами, их часто объединяют в группу параретровирусов. Однако здесь существует важное различие между ретровирусами и вирусами семейства Caulimoviridae. В отличие от ретровирусов они не интегрируют свой геном в хромосомы, так как их геном не кодирует фермента интегразы
Однако существуют виды семейства колимовирусов, такие как Petunia vein clearing virus, которые изредка (в основном в стрессовых условиях) могут интегрировать свой геном в хозяйственный геном[3]. Обычно такие провирусы часто называют эндогенными параретровирусами (EPRVs).
По данным Международного комитета по таксономии вирусов (ICTV), на март 2016 года в семейство включают 8 родов[4]:
Вид Rose yellow vein virus имеет необычную организацию генома, которое делает его уникальным видом[5].
Колимовирусы (лат. Caulimoviridae) — семейство ДНК-содержащих вирусов растений с механизмом обратной транскрипции и двуцепочечной ДНК, то есть вирусов, содержащих стадию обратной транскрипции в своём репликативном цикле.
花椰菜病毒科(Caulimoviridae)是環狀雙链DNA逆轉錄病毒的一科,包括以下属:
桿狀去氧核糖核酸病毒屬(Badnavirus)-代表種:鴨跖草屬萎黃(化)斑駁病毒(Commelina yellow mottle virus) 花椰菜鑲嵌(花葉)病毒屬(Caulimovirus)-代表種:花椰菜鑲嵌(花葉)病毒(Cauliflower mosaic virus) 水稻衰退(東格魯)桿狀樣病毒屬(Tungrovirus; Rice tungro bacilli-form-like viruses)-代表種:水稻衰退桿狀病毒(Rice tungro bacilliform virus) 大豆萎黃(退綠)斑駁樣病毒屬(Soymovirus; Soybean chlorotic mottle-like viruses)-代表種:大豆萎黃斑駁病毒(Soybean chlorotic mottle virus) 木薯葉脈鑲嵌樣病毒屬(Cavemovirus; Cassava vein mosaic-like viruses樹薯)-代表種:木薯葉脈鑲嵌病毒(Cassava vein mosaic virus) 牽牛花葉脈透明樣病毒屬(Petuvirus; Petunia vein clearing-like viruses碧冬茄脈明)-代表種:牽牛花葉脈透明病毒(Petunia vein clearing virus)